* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File - Nepal Pharmacy
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Protein phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Implicit solvation wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium transporter wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
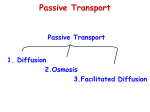
Mechanism of Transportation in a cell Or Transportation of molecules in a cell Presentation by: Mahendra Kandel Email: [email protected] For: Bachelor of Pharmacy, NIST Date: December 31, 2012 presentation by: Mahendra Kandel 1 Functions of Cell Membrane 1. Protect cell 2. Control incoming and outgoing substances 3. Maintain ion concentrations of various substances 4. Selectively permeable - allows some molecules in, others are kept out presentation by: Mahendra Kandel 2 Phospholipid Bilayer presentation by: Mahendra Kandel 3 Structure of the Cell Membrane Outside of cell Carbohydrate chains Proteins Lipid Bilayer Transport Protein Phospholipids Inside of cell (cytoplasm) Go to Section: presentation by: Mahendra Kandel 4 The Selectively Permeable Nature of Cell Membranes presentation by: Mahendra Kandel 5 Membrane Proteins • Each type of protein in a membrane has a special function – Adhesion proteins – hold to surface, cells – Receptor proteins – receive messages – Enzymes – speed up reactions – Transport proteins (active and passive) active – require energy to transport passive – no energy required for transport presentation by: Mahendra Kandel 6 Concentration and Gradients • Concentration – The number of molecules (or ions) of substance per unit volume of fluid • Concentration gradient – The difference in concentration between two adjacent regions – Molecules always move from a region of higher concentrationpresentation to one of lower concentration 7 by: Mahendra Kandel Types of Transportation • Passive Transport • Active Transport • Endocytosis (phagocytosis & pinocytosis) • Exocytosis presentation by: Mahendra Kandel 8 Passive Transport • No energy required • Move due to gradient – differences in concentration, pressure, charge • Move to equalize gradient – High moves toward low presentation by: Mahendra Kandel 9 Passive Transportation Weeee!!! high low presentation by: Mahendra Kandel 10 Types of Passive Transport 1. Diffusion 2. Osmosis 3. Facilitated diffusion presentation by: Mahendra Kandel 11 Diffusion • Movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. • Movement from one side of a membrane to another, un-facilitated presentation by: Mahendra Kandel 12 Diffusion • Molecules move to equalize concentration presentation by: Mahendra Kandel 13 Diffusion presentation by: Mahendra Kandel 14 Osmosis • Special form of diffusion • Fluid flows from lower solute concentration • Often involves movement of water – Into cell – Out of cell presentation by: Mahendra Kandel 15 Osmosis presentation by: Mahendra Kandel 16 Tonicity is a relative term • Hypotonic Solution - One solution has a lower concentration of solute than another. • Hypertonic Solution - one solution has a higher concentration of solute than another. • Isotonic Solution - both solutions have same concentrations of solute. presentation by: Mahendra Kandel 17 Solution Differences in a tissue/cells • solvent + solute = solution • Hypertonic – Solutes in cell more than outside – Outside solvent will flow into cell • Isotonic – Solutes equal inside & out of cell • Hypotonic – Solutes less than outside cell – Fluid will flow out of cell presentation by: Mahendra Kandel 18 presentation by: Mahendra Kandel 19 Facilitated Diffusion • Differentially permeable membrane • Channels (are specific) help molecule or ions enter or leave the cell • Channels usually are transport proteins • No energy is used presentation by: Mahendra Kandel 20 Types of Transport presentation by: Mahendra Kandel 21 Process of Facilitated Transport • Protein binds with molecule • Shape of protein changes • Molecule moves across membrane presentation by: Mahendra Kandel 22 Active Transport • Molecular movement • Requires energy (against gradient) • Example is protein pump This is gonna be hard work!! high presentation by: Mahendra Kandel low 23 1. Protein Pumps -transport proteins that require energy to do work • Example: Sodium / Potassium Pumps are important in nerve responses. presentation by: Mahendra Kandel 24 • Active transport in two solutes across a membrane • Na+/K+ pump • Protein shape change FLUID OUTSIDE CELL Transport protein First solute 1 First solute, inside cell, binds to protein 2 ATP transfers phosphate to protein 3 Protein releases solute outside cell 6 Protein releases second solute 25 into cell Second solute Phosphate detaches from presentation by: Mahendra Kandel protein 4 Figure 5.18 Phosphorylated transport protein Second solute binds to protein 5 Sodium-Potassium Pump presentation by: Mahendra Kandel 26 Endocytosis • Movement of large material – Particles – Organisms – Large molecules • Movement is into cells • Types of endocytosis – bulk-phase (nonspecific) – receptor-mediated (specific) presentation by: Mahendra Kandel 27 Bulk-phase endocytosis Extracellular fluid is captured in a vesicle and brought into the cell; the reverse of exocytosis • Receptor-mediated endocytosis – Specific molecules bind to surface receptors, which are then enclosed in an endocytic vesicle presentation by: Mahendra Kandel 28 Process of Endocytosis • Plasma membrane surrounds material • Edges of membrane meet • Membranes fuse to form vesicle presentation by: Mahendra Kandel 29 presentation by: Mahendra Kandel 30 Forms of Endocytosis • Phagocytosis – cell eating • Pinocytosis – cell drinking presentation by: Mahendra Kandel 31 Exocytosis • Reverse of endocytosis • Cell discharges material presentation by: Mahendra Kandel 32 Exocytosis • Vesicle moves to cell surface • Membrane of vesicle fuses • Materials expelled presentation by: Mahendra Kandel 33 Summary of Methods of Transport Across Membranes 1. Diffusion -passive transport - no energy expended 2. Osmosis - Passive transport of water across membrane 3. Facilitated Diffusion - Use of proteins to carry polar molecules or ions across 4. Active Transport- requires energy to transport molecules against a concentration gradient – energy is in the form of ATP presentation by: Mahendra Kandel 34 • Thank you! presentation by: Mahendra Kandel 35