* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Viruses
Epigenetics in stem-cell differentiation wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
DNA polymerase wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Bisulfite sequencing wikipedia , lookup
Genealogical DNA test wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom National DNA Database wikipedia , lookup
DNA damage theory of aging wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid double helix wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
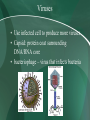
Viruses Viruses • Use infected cell to produce more viruses • Capsid: protein coat surrounding DNA/RNA core • bacteriophage – virus that infects bacteria Viral Infections Lytic Infection • after entering the cell, host cell make 1000’s of copies of viruse’s DNA • new virus particles are made • the infected cell then lyses, or busts • 100’s of virus particles are released Viral Infections Lysogenic Infection • Prophage: viral DNA become part of the host’s DNA • viral DNA is copies with host’s DNA • When the prophage is activated, the cell enters the lytic cycle Retroviruses • • • • RNA In host cell, makes a DNA copy of RNA its DNA is inserted into the host’s DNA AIDS Are Viruses Alive? • Not Alive – – – – no response to the environment does not obtain or use energy no growth or development reproduces only with a host cell