* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
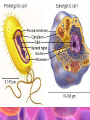
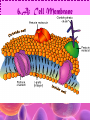
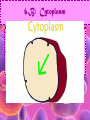
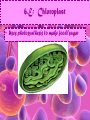
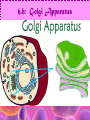
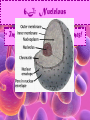
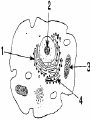
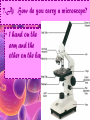
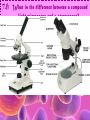
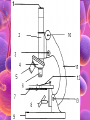
Cell Study Guide 1. Define Cell • Basic Unit of Life 2. What are the 3 parts of the cell theory • All cells arise from existing cells • Cells are the basic unit of life • All organisms are made of one or more cells Schleiden, Schwann and Virchow 3. Describe the difference between prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells and give an example of each • Prokaryotic cells (bacteria cells) are simple cells that lack a nucleus and membrane bound organelles • Eukaryotic cells (animal and plant cells) are complex cells with nuclei and organelles – eukaryotic cells all have cell membrane, cytoplasm ad nucleus. 4. Compare and contrast plant cells and animal cell • Plant Cells contain cell walls, chloroplasts and a large central vacuole • Animal Cells contain centriole • Both plant and animal cells contain: cell membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus and many organelles 5. Define ORGANELLE • Any tiny structure that performs a specialized function or job in the cell 6.A: Cell Membrane • Gatekeeper-allows only certain things to enter or leave the cell • Made of a Phospholipid Bilayer • Fluid mosaic theory describes the modern view of the cell 6.B: Cytoplasm • Jelly-like substance between cell membrane and the nucleus. • All organelles are suspended in this substance 6.C: Chromosomes • Contain genetic blueprints/DNA that control all of a cell’s activities 6.D: Ribosomes • Found free floating OR on the Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum • Produces proteins 6.E: Chloroplast • Uses photosynthesis to make food/sugar 6.F: Vacuole • Store water, ions and waste products 6.G: Mitochondria • ENERGY • Cells that require MORE energy contain MORE mitochondria 6.h: Golgi Apparatus • Packages substances up for shipment out of the cell 6.I: Nucleus • Control center of the cell – all of the cells activities are directed by this organelle 6.J: Nuclelous • Inside nucleus-Makes Ribosomes! 6.K: Endoplasmic Reticulum • Smooth ER: Transports and processes lipids • Rough ER: Transports and processes lipids 6.L: Centriole • Helps organize spindle fibers during cell division 7.A: How do you carry a microscope? • 1 hand on the arm and the other on the base 7.B: When do you use the coarse adjustment? • Use while scanning or on low power to locate the object you are trying to observe. Never use on high power!!! 7.C: How do you find the total magnification of a microscope? • Multiply the magnification of the eyepiece times the magnification of the objective lens you are using. 7.D: Why do we stain items we observe with a microscope • Stains darken light objects making them easier to observe 7.E: How does the “field of view” change when you change the magnification? • The higher the magnification, the smaller the field of view 7.f: What is the difference between a compound light microscope and a stereoscope? • Compound light looks at smaller objects, shows images in 2D and shows the image backwards • Stereoscope looks at larger objects, shows images in 3D and show the image the way that it truly is.