* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download THE CELL
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
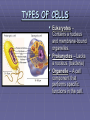
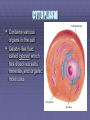
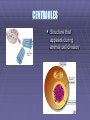
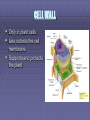
THE CELL “The smallest unit that can carry out all the processes of life.” Scientists Who Discovered the Cell Discovery of the Cell ROBERT HOOKE First to observe cells. He examined cork cells. “These little boxes reminded him of the small rooms in which monks lived, so he called them cells.” Discovery of the Cell Anton van Leeuwenhoek – First person to examine living cells & father of microscopy Matthias Schleiden – “All plants are composed of cells.” Theodore Schwann – “All animals are composed of cells.” Rudolf Virchow – “All cells come from existing cells.” The Cell Theory Schleiden, Schwann, & Virchow All living things are composed of one or more cells. Cells are organisms’ basic units of structure & function. Cells come from existing cells. CELL DIVERSITY 1. Size Cells range in size from .2 um to 2 m. Average plant & animal cells are 10 to 50 um in diameter. 2. Shape Cuboidal & spherical. 3. Internal Organization Different Organelles TYPES OF CELLS Eukaryotes – Contains a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles. Prokaryotes – Lacks a nucleus. (bacteria) Organelle – A cell component that performs specific functions in the cell. ORGANELLES Nucleus Cell Membrane Cytoplasm Ribosomes Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Golgi Apparatus Mitochondria Lysosomes Cytoskeleton Microtubules & Microfilaments Cilia Flagella The Nucleus Directs activities of the cell. Contains DNA. Nucleolus – synthesis of ribosomes. Nuclear pores Nuclear envelope Nucleoplasm DNA Deoxyribonucleic acid Encodes information important for the synthesis of proteins. CYTOPLASM Contains various organs in the cell Gelatin-like fluid called cytosol which has dissolved salts, minerals, and organic molecules CELL MEMBRANE Made of lipids & proteins. Provides shape & flexibility. Selectively Permeable - a complex barrier that keeps out some molecules & allows others through. RIBOSOMES Carry out protein synthesis. Attached ribosomes attached to Rough ER; produce proteins to be exported by the cell. Free ribosomes produce proteins for the cell. ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum - (ER) - A membrane system covered with ribosomes; aids in protein synthesis. Smooth ER - Few or no ribosomes; intracellular pathway for proteins. GOLGI APPARATUS System of membranes. Processing, packaging, & secreting organelle of the cell. MITOCHONDRIA “Powerhouse of the cell.” Carries out cellular respiration. LYSOSOMES Contains digestive enzymes. Digests food & disease-causing bacteria. CYTOSKELETON Provides a structural framework for the cell. Microtubules - long, slender protein tubes Microfilaments - fine protein threads. CILIA & FLAGELLA Function in movement. Composed of proteins. Cilia - small & hair-like; covers entire surface of the cell. Flagella - long & slender; found singly or in pairs. VACUOLES Store substances inside the cell. Plant cells have large central vacuoles. CENTRIOLES Structure that appears during animal cell division CELL WALL Only in plant cells Lies outside the cell membrane Supports and protects the plant PLASTIDS Convert solar energy into chemical energy. Chloroplast - contain green pigments Leucoplast - store food, such as starches. Chromoplast synthesize & store other pigments. Plant cells only!! CHLOROPLASTS Found in plant cells only Where the energy of sunlight is converted into chemical energy during photosynthesis Contain green pigment called chlorophyll DIFFERENCES BETWEEN PLANT & ANIMAL CELLS ANIMAL CELLS Centrioles Small vacuoles PLANT CELLS Plastids Large central vacuole Cell Wall