* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download History of Cell Discovery
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
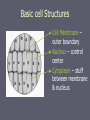
History of Cell Discovery Chapter 4 Microscope view of cells ► Robert Hooke – first to see cells designed microscope that he was able to view cork cells with (1665). ►Named “Cells” because they look like monk quarters Cells with stone beds Microscope view of cells Anton Van Leeuwenhoek – first to see living cells. ► improved design, and was able to view red blood cells and bacteria. Called them "animalicules" Scientists of Cell Theory ► Theodore Schwann – zoologist who observed that the tissues of animals had cells (1839) Scientists of Cell Theory ► Mattias Schleiden – botanist who observed that the tissues of plants had cells (1845) Scientists of Cell Theory ► Rudolf Virchow – reported that every living thing is made up of cells, and that these cells must come from other cells. Cell Theory 1. All living things are made of one or more cells. 2. Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in organisms. (the smallest unit that can perform life functions) 3. All cells come from pre - existing cells. Terms ► Cell – the smallest unit that can carry on the processes of life. ► Unicellular cell – consists of only one ► Multicellular – consists of more than one cell Basic cell Structures ► Cell Membrane – outer boundary ► Nucleus – control center ► Cytoplasm – stuff between membrane & nucleus Two Basic Cell Types ►Prokaryotic – lacks internal organelles surrounded by membranes Has a cell membrane & a cell wall Has NO nucleus. ►Means “before the nucleus” Usually Unicellular organisms Ex: Bacteria Why should we care about prokaryotes? ► Benefits prokaryotes (bacteria) provide: Bacteria in your stomach aid in digestion Provide immunity Break down waste Food production (dairy products and anything fermented) Used in production of medicine (i.e. insulin) ► You have 1 trillion cells in your body. There are 10 trillion bacterial cells living on/in your body ► 100 times more bacterial DNA on us or in us affecting us than our own DNA (so we're basically 99% bacteria). Two Basic Cell Types ►Eukaryotic – contains internal membrane bound organelles. Has a nucleus Has a cell membrane Usually multicellular organisms Ex: Plants, animals, and protists