* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Parts - Garnet Valley
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
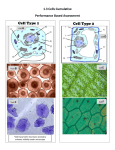
Chapter 1- Sec. 2 Cell Parts Life Science A World of Cells Cell- is the basic unit of structure in living things that carry out life processes. – Many cells are about 0.01 mm long Look at your Hand… – One square centimeter of your skin’s surface contains more than 100,000 cells. Cells are Diverse!!! Cells come in different sizes and their shape can tell you something about its function. 2 Types of Cells 1. Prokaryotic Cells- no internal organelles - 2. Genetic Material is located in cytoplasm Single-celled organisms Eukaryotic Cells- contain organelles - Genetic Material is located in nucleus - some Unicellular and Multicellular organisms What’s the Difference? Open your textbooks to Page 20 and see the differences between a Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cell. Cells contain structures that carry out specific functions inside of the cell. There are ONLY TWO types of Eukaryotic Cells that we will discuss in class!!! See page 22 We will do multiple labs to see these parts Plants and Animals have EUKARYOTIC CELLS!!! Lets look at the “parts” that make up eukaryotic cells… Surrounding the Cell… Cell Membrane- protective layer around cells that allows material to enter and exit the cell. – Allows food, oxygen/carbon dioxide into the cell and waste products out of the cell. Around Plant Cells… Cell Wall- tough outer covering that protects and supports PLANT cells only. – Made up of a strong material called Cellulose. Inside the cell… Cytoplasm- clear, gelatin-like substance that flows inside the cell membrane. Throughout the cytoplasm is a framework called… Cytoskeleton- helps the cell maintain or change its shape Inside of a Cell What are Organelles??? Organelles- “scientific” word used to describe any part of a cell – Float throughout the cytoplasm – Each organelle or “part” of the cell has a specific function and job Process Information Nucleus- the control center of the cell – Contains the instructions & information a cell needs to function – These “instructions” are made of DNA or Chromatin Nucleus Energy Providing Organelles Mitochondria- “powerhouse” of the cell that releases energy from food. – Found in both plant & animal cells Chloroplasts- green organelles only in plant cells that contain chlorophyll – Uses energy from sun to make sugar STOP HERE Manufacturing Organelles Ribosomes- grain-like bodies that make proteins for cell activities. – How you grow & repair Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)- a series of smooth or rough membranes that transports or carries proteins or other materials from one part of the cell to another. Manufacturing Organelles Golgi Bodies- stacked, flattened membranes that sort and package proteins. – Packages cell material for transport into vesicles. Storage & Recycling Organelle Vacuoles- “storage” organelle that stores water, waste, food, and other materials. – Most plant cells have one large vacuole. – Animal cells have a few Lysosomes- “clean up crew” that contains chemicals to break down materials (food/wastes) in a cell. – Recycling Organelle – When a cell dies, it releases chemicals that digests or eats the cell From Cell to Organism