* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download A View of the Cell
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
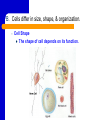
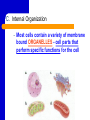
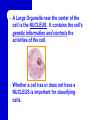
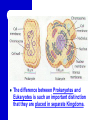
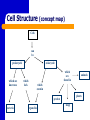
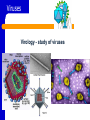
A View of the Cell Life is Cellular Discovering the Cell Robert Hooke – used a microscope to study cork – coined the term “cell” Anton van Leeuwenhoek – first person to discovered life in water using a microscope I. Introduction to the Cell A. Cell Theory – All organisms are made up of one or more cells. – Cells are the basic unit of structure & function in organisms. – All cells come from preexisting cells. B. Cells differ in size, shape, & organization. – Cell Size Small cells function more efficiently than large cells. Smaller is BETTER! Large cells cannot function efficiently in the transport of materials & waste into and out of the cell. B. Cells differ in size, shape, & organization. – Cell Shape The shape of cell depends on its function. C. Internal Organization – Most cells contain a variety of membrane bound ORGANELLES - cell parts that perform specific functions for the cell – A Large Organelle near the center of the cell is the NUCLEUS. It contains the cell’s genetic information and controls the activities of the cell. – Whether a cell has or does not have a NUCLEUS is important for classifying cells. II. Prokaryotes Vs. Eukaryotes EUKARYOTES – ORGANISMS WHOSE CELL OR CELLS CONTAIN A NUCLEUS AND OTHER MEMBRANE-BOUND ORGANELLES. – MORE COMPLEX – CAN BE HIGHLY SPECIALIZED – UNICELLULAR OR MULTICELLULAR – PLANTS, ANIMALS, FUNGI, PROTISTS Prokaryotes Vs. Eukaryotes PROKARYOTES – ORGANISMS WHOSE CELLS DO NOT HAVE A NUCLEUS AND OTHER MEMBRANE-BOUND ORGANELLES. – SMALLER AND SIMPLER – UNICELLULAR ORGANISMS SUCH AS BACTERIA AND BLUE-GREEN ALGAE The difference between Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes is such an important distinction that they are placed in separate Kingdoms. Cell Structure (concept map) Cells can be prokaryotic which are known as eukaryotic which lack which are found in which contain plants protists bacteria animals organelles fungi WRAP-UP QUESTIONS What is the smallest most basic unit of life? Where is DNA in eukaryotes? …prokaryotes? Why would you need a microscope to see a prokaryotic organism? What are the 3 parts of the cell theory? Where do viruses fit in the cell theory? Viruses Virology - study of viruses Viral Characteristics Non Not living made up of cells Cannot grow or replicate on their own Must be reproduced in living cells