* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CFA Remediation
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
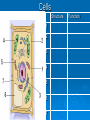
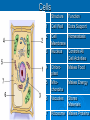
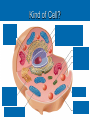
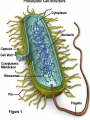
PA Remediation Goals 2.01, 2.02, 2.04 Organic Compounds Carbohydrates Proteins Lipids Nucleic Acids Made of? (elements) Monomer Polymer Test Use N/A Organic Compounds Made of? (elements) Monomer Polymer Carbohydrates Proteins Lipids Nucleic Acids C, H, O 1:2:1 ratio C, H, O, N C, H, O No Ratio C, H, O, N, P Simple Sugar C6H12O6 Starches Amino Acids Protein Fatty Acids Nucleotide Lipids: steroid, waxes Test Benedict’s RNA & DNA Biuret’s Brown Paper Bag N/A Structural Elements & Enzymes Structural Elements Heredity Information (Monomer) Lugol’s(Polymer) Use Energy Cell Membranes Which of the following macromolecules found in animal tissues functions to insulate and help animals conserve heat? • Carbohydrates • Lipids • Proteins • Nucleic acids Carbon is important to living things because: • It metabolizes easily, creating a quick energy source • It is abundant on the Earth’s surface • It can form 4 covalent bonds with other atoms • It has 12 protons and neutrons Nucleotides are to nucleic acids as amino acids are to: A. DNA B. Polypeptides C. Proteins D. Carbohydrates When Lugols turns dark blue to black in color, it is an indicator for the presence of what compound? A. Carbohydrates B. Lipids C. Proteins D. Nucleic acids Enzymes Enzymes are proteins used to speed up reactions. (catalyst) specific to the reactions they catalyze. reusable. Enzymes What effects them and how? Temperature • Optimal point, denatures when too hot or cold usually pH • Optimal point, denatures when to acidic or basic usually Concentration • As concentration increases so does reaction rate What are enzymes? • Catalysts used by living things • Catalysts used in all reactions • Chemicals used to increase activation energy • Fats used by living things to help speed up chemical reactions How does an enzyme affect a chemical reaction? • It increases the amount of product formed • It decreases the amount of product formed • It increases the activation energy • It decreases the activation energy. One enzyme can facilitate the reaction of many substrate molecules. Why does an enzyme have this ability? • Enzymes are super charged. • Enzymes are reusable. • Enzymes are made from proteins. • Enzymes are disassociated. The graph shows that temperature • Has no affect on enzyme activity • Has an optimum where the enzyme works best • Can denature the enzyme • Both B and C are correct The Cell Theory States That all Living Organisms Are: • Made of one or more cells • Cells are the basic unit of structure and function • Cell come only from pre-existing cells Cells Structure 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Function Cells Structure Function 1 Cell Wall Extra Support 2 Cell Homeostasis Membrane 3 Nucleus Controls All Cell Activities 4 Chloroplast Makes Food 5 Mitochondria Makes Energy 6 Vacuoles Stores Materials 7 Ribosome Makes Proteins Kind of Cell? Plants vs. Animal Plant Cell Wall Chloroplasts Large vacuoles Animal Centrioles Lysosomes Prokaryotic Vs. No nucleus or membrane bound organelles Eukaryotic Nucleus and membrane bound organelles Cell wall Cell membrane Cytoplasm Ribosomes Flagella/cilia Chromatin Cell wall Cell membrane Cytoplasm Ribosomes Flagella/cilia Hierarchy of Cell Organization Organic compounds Organelles Cells Tissues Organs Organ systems Cell Communication Cells communicate in a variety of ways….. Direct contact through cytoplasmic bridges between the cells They share cytoplasm and its contents Chemical signals Chemical signals are released from one cell and travel to another cell These signals influence the activity of the second cell Examples include hormones and neurotransmitters. The mitochondrion of the cell: A. Has only one membrane B. Has no membrane C. Is circular D. Is where cellular respiration occurs Ribosomes: A. Are the site of protein synthesis B. Are made by other ribosomes C. Have their own DNA D. None of the above A(n) ________ is a group of different tissues that work together to perform a certain function. A. Organ system B. Organ C. Cell D. Organelle Structures that support and give shape to plant cells are: A. Microbodies B. Golgi bodies C. Nucleus D. Cell walls Which of the following is part of the cell theory? All cells: A. Are eukaryotic B. Are prokaryotic C. Have nuclei D. Come from other cells The storage of hereditary information in a eukaryotic cell is in the: A. Cytoplasm B. Nucleus C. Centrioles D. Lysosomes