* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Growth and Division
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Spindle checkpoint wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
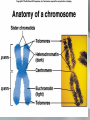
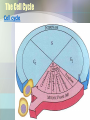
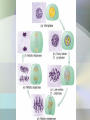
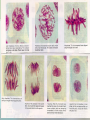
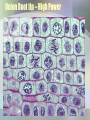
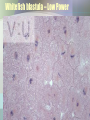
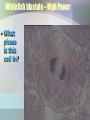
Cell Growth and Division Chapter 10 Why do cells divide? • Cells divide to allow the organism to grow and to repair damaged tissue • Cells grow, then divide. Why don’t they keep growing? • Large cells do not have enough DNA to function. • Large cells could not diffuse oxygen and nutrients efficiently. *Agar block lab* Cell division in Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes: • Prokaryotes – single chromosome is copied and the cell splits. Binary fission. • Eukaryotes – All chromosomes must be copied into sister chromatids, held together by a centromere. The copies are then split apart in a process called MITOSIS. The cytoplasm is then split by CYTOKINESIS. The Cell Cycle Cell cycle Main steps of mitosis: “IPMAT” • Interphase – The cells grows and replicates DNA and centrioles. • Prophase – DNA wraps up into chromosomes. The nuclear membrane dissolves. • Metaphase – Chromosomes line up. Spindle fibers created by the centrioles attach to the centromere.. • Anaphase – The will spindle fibers will pull the sister chromatids apart • Telophase – chromosomes at opposite ends, the nuclear membrane re-forms. Live video of mitosis: •Cell division •Newt cell division Mitosis Lab Microscope Images • Onion Root tip • Low Power Onion Root tip – High Power Whitefish blastula – Low Power Whitefish blastula – High Power • What phase is this cell in? Duration of mitosis phases…