* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell growth and division powerpoint
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
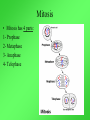
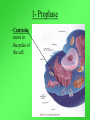
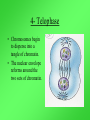
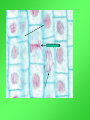
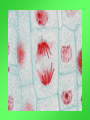
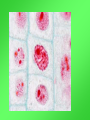
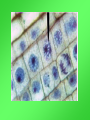
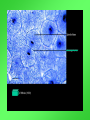
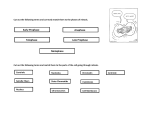
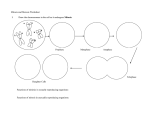
Cell Growth and Division When we grow up, what’s really happening to our cells? Cell Growth and Division Do we grow by getting more cells? Or do the cells we already have get bigger? Cell Growth • Cells can only grow to a certain size before they have to divide. • An adult and a baby have the same size of cells. Adults just have more cells. • Your body makes about 24,000,000,000 new cells each day. Life is made of cells video Why can’t cells just get bigger? There are two reasons that cells have to divide as they grow. 1- DNA overload 2- Exchanging materials DNA Overload • The bigger cells get, the harder it is for DNA to be used by the entire cell. • Like a small town library as the town grows bigger. Exchanging materials • The cell membrane has to transfer items in and out of the cell. • As the cell grows, the volume increases faster than the surface area does. • Like the roads leading into or out of a town. The cell cycle • The cell cycle (life cycle of a cell) has 4 main parts: – – – – G1 phase S phase G2 phase M phase The cell cycle • Anytime the cell is not dividing, it is in Interphase – During interphase the cell grows, copies its DNA, and gets ready to divide. • M phase is when the cell divides Cell Division • During cell division the cell actually divides into two identical cells. Mitosis • Mitosis has 4 parts: 1- Prophase 2- Metaphase 3- Anaphase 4- Telophase 1- Prophase • During Prophase: – Chromosomes condense and become visible. 1- Prophase – Centrioles move to the poles of the cell. 1- Prophase – The nuclear envelope breaks down. 2- Metaphase • During Metaphase, the chromosomes line up across the center of the cell. 3- Anaphase • During anaphase, the chromosomes split apart and move to opposite sides of the cell. • Anaphase continues until the chromosomes stop moving. 4- Telophase • Chromosomes begin to disperse into a tangle of chromatin. • The nuclear envelope reforms around the two sets of chromatin. Mitosis • Mitosis is now complete! • Remember: Mitosis: 1- Prophase 2- Metaphase 3- Anaphase 4- Telophase Quiz time!!! Which part of mitosis does each of the following pictures represent?