* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Osmosis Diffusion Notes
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
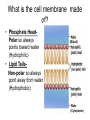
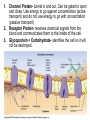
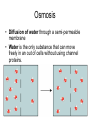
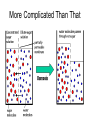
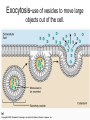
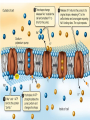
Cell Membarane • Also known as Plasma Membrane and Phospholipid Bi-layer • Defines the shape of the cell. • Maintains Homeostasis (controls what goes in and out) What is the cell membrane made of? • Phosphate HeadPolar so always points toward water (Hydrophilic) • Lipid TailsNon-polar so always point away from water (Hydrophobic) (Blood) (Cytoplasm) 1. Channel Protein- tunnel in and out. Can be gated to open and close. Use energy to go against concentration (active transport) and do not use energy to go with concentration (passive transport) 2. Receptor Protein- receives chemical signals from the blood and communicates them to the inside of the cell. 3. Glycoprotein + Carbohydrate- identifies the cell so it will not be destroyed. Key Words • Solution- combination of a solute and a solvent. • Solute- Substance that is dissolved in a solvent (i.e. salt, sugar etc) • Solvent- Substance that other substances are dissolved into (i.e.- water) • Concentration Gradient- Difference in solute concentration from one side of the membrane compared to the other. Diffusion • Movement of a solute within a solvent from high concentration to low concentration • EXAMPLE- Food coloring (Solute) moving from the high concentration of a drop to the low concentration of the water (Solvent). Osmosis • Diffusion of water through a semi-permeable membrane • Water is the only substance that can move freely in an out of cells without using channel proteins. More Complicated Than That Why Water Moves • Hypertonic SolutionThe outside of the cell has more solute than inside the cell • RESULT- Water moves out and the cell shrinks. Why Water Moves • Hypotonic SolutionThe outside of the cell has less solute than inside the cell. • RESULT- Water moves in and the cell swells/bursts. Why Water Moves • Isotonic SolutionWhen there is an equal amount of solute inside and outside the cell • RESULT- Water moves both in and out of the cell at the same rate and the cell stays the same Moving Stuff Passive TransportMovement across a cell membrane that goes with concentration gradient and does not use any energy Examples- Osmosis and Facilitated Diffusion Moving Things • Active TransportMovement across a membrane going against concentration gradient where energy is needed • ExamplesEndocytosis and Exocytosis Endocytosis- use of vesicles to transport large objects into the cell. Exocytosis-use of vesicles to move large objects out of the cell. Sodium Potassium Pump Active Transport • Sodium Potassium Pump moves 3 Na+ ions out of the cell and brings 2 K+ ions into the cell creating + out side and a – inside. • This is moving against concentration so it requires ATP (Energy) • When the nerve fires Na+ ion channels open in the membrane and Na+ floods in changing charge on the inside only to be reset by the Na/K pump. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=PimDC1txWw&index=2&list=FLEezLUm-pa3vfMmQGp1aPTQ https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SdUUP2pMmQ4&index=1&list=FLE ezLUm-pa3vfMmQGp1aPTQ