* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download How things get in and out of a Cell HOMEOSTASIS
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
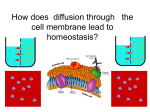
How things get in and out of a Cell HOMEOSTASIS Maintaining a constant internal environment • the human body maintains homeostasis through body temperature, blood pressure, heart rate, oxygen balance and water balance, and waste disposal. THESE ARE ALL EXAMPLES OF HOMEOSTASIS. • EVERY organism MUST maintain homeostasis. • Each INDIVIDUAL CELL must maintain homeostasis. - Cells do this by controlling what enters it and what goes out of it. Which cell structure aids the cell in maintaining homeostasis ? THE PLASMA MEMBRANE ! PASSIVE TRANSPORT Allowing substances in or out of the cell WITHOUT requiring energy. Types of Passive Transport 1. DIFFUSION - Movement of stuff from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration - diffusion will occur until a DYNAMIC EQUILIBRIUM (concentration of particles are equally spread out) is reached. Rate of Diffusion is affected by : temperature concentration pressure Diffusion is occurring. (the particles of sugar are spreading from high concentration to lower concentration) An equilibrium has been reached. (the particles of sugar are evenly spread out.) Another type of PASSIVE TRANSPORT is … OSMOSIS - Diffusion of water * Osmotic Pressure = the pressure that is exerted by H2O on the cell. * PLANTS have TURGOR PRESSURE (pressure exerted by stuff in the cell on the cell wall) * PLASMOLYSIS - The loss of turgor pressure (when this happens, the plant wilts) QuickTime™ and a Sorenson Video decompressor are needed to see this picture. ACTIVE TRANSPORT allowing substances in and out of cell USING energy - usually moves stuff in or out AGAINST the diffusion gradient (a.k.a. - the concentration gradient). * The diffusion gradient refers to the different levels of concentration inside and outside of the cell When a cell uses ACTIVE TRANSPORT, things CAN move from low to high concentrations. Types of Active Transport 1. ENDOCYTOSIS movement of stuff INTO the cell using energy - cell use endocytosis to take in more food, minerals, and ions that diffusion allows them to. 2. EXOCYTOSIS movement of stuff OUT OF the cell using energy - lipids, wastes, hormones, and enzymes leave the cell by exocytosis.