* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Cell
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
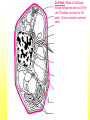
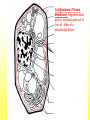
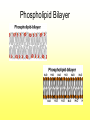
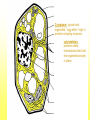
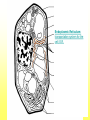
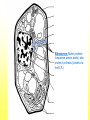
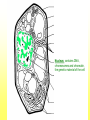
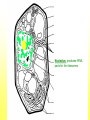
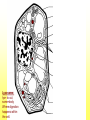
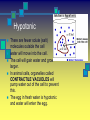
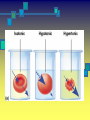
The Cell Plant Cell Cell Wall: Made of Cellulose; Allows things into and out of the cell; Provides structure to the plant. Does not exist in animal cells. Cell Membrane (Plasma Membrane): Regulates what goes in and what goes out of the cell. Made of a phospholipid bilayer. Phospholipid Bilayer Cytoplasm: cytosol and organelles; “egg white”; high in proteins including enzymes cytoskeleton: proteins called microtubules that hold the organelles loosely in place Endoplasmic Reticulum: transportation system for the cell; E.R. Nuclear Membrane (Nuclear Envelope): regulates what goes in and out of the nucleus: phospholipid bilayer Ribosomes: Make proteins (sequence amino acids); aka protein synthesis (travels via the E.R.) Nucleus: contains DNA, chromosomes and chromatin, the genetic material of the cell Nucleolus: produces rRNA, parts for the ribosomes Chromatin: DNA/chromosomes; invisible until it coils up Vacuoles: storage for the cells; food vacuoles, water vacuoles, etc.; garage Mitochondria: cell respiration; C6H12O6 + 6O2 = 6CO2 +6H2O = 38 ATP Converts food into ATP Chloroplasts: Only in plant cells. Perform photosynthesis in the presence of light turning sunlight energy into chemical energy; 6CO2 +6H2O = C6H12O6 + 6O2 Golgi Apparatus/Golgi Body: Flattened sacs that act like the Post Office for the cell. They package and ship materials outside the cell or to other cells. Golgi Bodies: Lysosome: lys= to cut; some=body Where digestion happens within the cell. Osmosis Diffusion of water across a membrane Does not require ATP Hyper Above Ex. Hyperactive Hypo Below Ex. Hypodermic needle (above/over active) (below + skin) Iso Equal Ex. Isobar (same barometric pressure) Hypertonic There are more solute (salt, sugar, etc.) molecules outside the cell Water moves towards the higher solute concentration “salt sucks” Cells shrink as they lose water. Egg in salt water is hypertonic and will lose water. Hypotonic There are fewer solute (salt) molecules outside the cell water will move into the cell. The cell will gain water and grow larger. In animal cells, organelles called CONTRACTILE VACUOLES will pump water out of the cell to prevent this. The egg in fresh water is hypotonic and water will enter the egg. Isotonic Concentration of solute (salt) is equal on both sides. Water will move back and forth across membrane. No change on the overall amount of water on either side.