* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Passive Transport: Osmosis and Diffusion
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
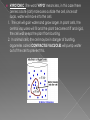
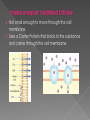
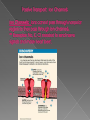
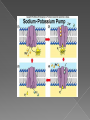
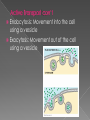
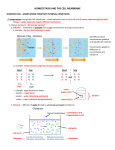
In 1838. The Cell Theory: All living things are made of cells. Cells are the basic units of life. Cells come only from other cells. Types of cells Prokaryotes - cells with no nucleus or organelles with membranes. Bacteria and blue-green bacteria are prokaryotic cells. Eukaryotes - cells that contain a nucleus and organelles surrounded by a membrane. The cells of protozoa, algae, fungi, plants, and animals are eukaryotic cells Passive transport: Caused by a random movement of molecules. They are constantly vibrating which causes them to collide and bounce off of each other. ** NO ENERGY USED** Diffusion: Movement of substances from high amount to low amount until equilibrium is reached. Osmosis: type of diffusion but moves only WATER from high amount to a low amount until equilibrium is reached. -- Movement of water through the cell membrane. •A complex barrier of lipid molecules separating the cell from its external environment. •These molecules can move apart to allow larger particles to move in or out of the cell. Selectively Permeable - membranes that allow some things through, the cell membrane is selectively permeable, water and oxygen move freely across the cell's membrane, by diffusion ISOTONIC: If the concentration of solute (salt) is equal on both sides, the water will move back in forth but it won't have any result on the overall amount of water on either side. "ISO" means the same HYPERTONIC: The word "HYPER" means more, in this case there are more solute (salt) molecules outside the cell, which causes the water to be sucked in that direction. 1. In plant cells, the central vacuole loses water and the cells shrink, causing wilting. 2. In animal cells, the cells also shrink. 3. In both cases, the cell may die. 4. This is why it is dangerous to drink sea water - its a myth that drinking sea water will cause you to go insane, but people marooned at sea will speed up dehydration (and death) by drinking sea water. 5. This is also why "salting fields" was a common tactic during war, it would kill the crops in the field, thus causing food shortages. A simple rule to remember is: Salt is a solute, when it is concentrated inside or outside the cell, it will draw the water in its direction. This is also why you get thirsty after eating something salty. HYPOTONIC :The word "HYPO" means less, in this case there are less solute (salt) molecules outside the cell, since salt sucks, water will move into the cell. 1. The cell will gain water and grow larger. In plant cells, the central vacuoles will fill and the plant becomes stiff and rigid, the cell wall keeps the plant from bursting 2. In animal cells, the cell may be in danger of bursting, organelles called CONTRACTILE VACUOLES will pump water out of the cell to prevent this. hypertonic Hypotonic Not small enough to move through the cell membrane. Uses a Carrier Protein that binds to the substance and carries through the cell membrane. USES ENERGY!!! Called ATP Goes against concentration gradient, meaning… it moves substance from a low amount to a high amount. Some use pumps: Example Sodium-Potassium pump. Transports 3 NA out and 2 K in. Endocytosis: Movement into the cell using a vessicle Exocytosis: Movement out of the cell using a vessicle