* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Structure & Function
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
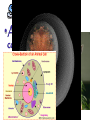
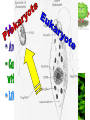
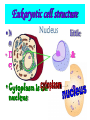
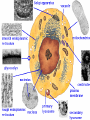
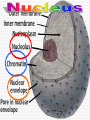
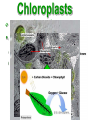
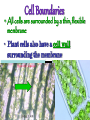
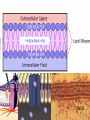
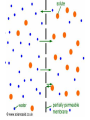
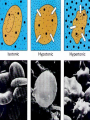
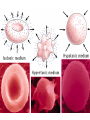
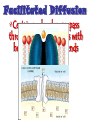
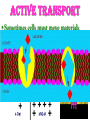
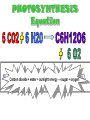
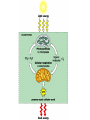
•All living things are composed of cells •Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in living things • New cells come from other cells Prokaryotes vs. Eukaryotes Prokaryotes… •Do not contain a nucleus •Are smaller and simpler •Carry out every activity associated with living things •Like bacteria! Which one am I ??? Eukaryotes • Usually larger and more complex •Highly specialized • Genetic material is separated from the rest of the cell in a nucleus •Can be a single cell or multicellular organism Examples Eukaryotic cell structure •Made up of organelles or “little organs” • Divided into 2 parts: nucleus & cytoplasm •Cytoplasm is outside the nucleus Nucleolus •Where ribosomes are made Ribosomes • Are made of RNA and protein • Assemble proteins •Protein assembly instruction comes from the nucleus • Cells active in protein synthesis have many ribosomes Endoplasmic reticulum •Makes and exports proteins and lipids • Rough ER makes proteins, so its covered in ribosomes! • Smooth ER makes enzymes Golgi Apparatus Lysosomes •Clean up crew, remove junk! • Digest or break down lipids, carbohydrates, proteins and old organelles • Filled with enzymes • Converts food into compounds the cell uses •Mitochondria are from the egg cell, so thank your MOM! Chloroplasts • Found in plant cells •Capture energy from the sun and convert it into chemical energy… Photosynthesis Cilia & Flagella Cell Boundaries • All cells are surrounded by a thin, flexible membrane • Plant cells also have a cell wall surrounding the membrane Cell Membrane •Regulates what comes in & out of the cell •Provides structure and support •Made of a lipid bilayer which provides a strong flexible barrier • The lipid bilayer has carbohydrates AND proteins embedded within! •Located outside cell membrane in plant, algae, fungi and prokaryotic cells • What Usually made of carbs & protein am I??? •Plant cell walls are made of cellulose • Provides protection and support • When particles move from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration • Equilibrium occurs when the concentration of solute (particles) is the same throughout The Dye = Solute Water= Solvent • Water passes easily across membranes • Osmosis is the diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane Isotonic Facilitated Diffusion •Certain molecules can pass through cell membranes with help from protein friends Active Transport •Sometimes cells must move materials in the direction opposite diffusion • This requires energy • Transport proteins or “pumps” help this happen Chemical Energy & ATP •Adenosine triphosphate helps cells store & release energy 8-2 Photosynthesis: An Overview • Plants use energy from the sun to convert water and carbon dioxide into carbohydrates (sugars & starches) and release oxygen as a waste product PHOTOSYNTHESIS Equation NO PANICKING!!! •In addition to water and carbon dioxide, photosynthesis requires light and chlorophyll, a pigment found in chloroplasts What happens to all that glucose that was made in photosynthesis? •Serves as a source of raw material for cells to make new molecules • Provides ENERGY Cellular Respiration • A process that releases energy by breaking down glucose & other food molecules with oxygen present You go to Thenwork you save to the $$ for your future! make money! Remembe r me?? I’m ATP! Anaerobic Cellular Respiration • Pyruvic acid doesn’t enter the mitochondria when oxygen isn’t present • Instead, fermentation occurs in the cytoplasm • There are 2 types: 1) Alcoholic 2) Lactic Acid