* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 1. Write scientific method down in order and describe each step
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
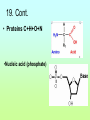
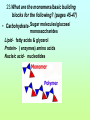
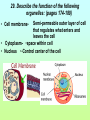
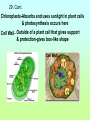
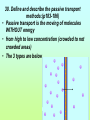
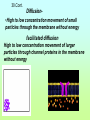
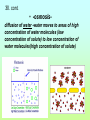
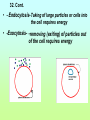
1st Semester Midterm 18.What are the 4 main macromolecules and give their main function? (pages 45-47) • • • • Carbohydrates- energy Proteins- Forms bones & muscle Lipids- stores fat Nucleic acid- DNA 19.Draw the 4 different macromolecule structures. (pages 45-47) • (lipid-row of carbons with H above and below) •Carbohydrate C+H+O 19. Cont. • Proteins C+H+O+N •Nucleic acid (phosphate) 20. What are the SPONCH elements? (notes) • Sulfur, Phosphorus, Oxygen, Nitrogen, Carbon & Hydrogen 21. What are the pH levels and what they mean? (p.43) • 0-3 • Very • acidic 4-6 slightly acidic 7 neutral 8-10 slightly basic 11-13 very basic 22. Define the terms: (page 45) • Monomer- smallest unit-that combines to make polymers Polymer- large compound made up of monomers Macromolecule- giant molecules made of many polymers 23.What are the monomers/basic building blocks for the following? (pages 45-47) • Carbohydrate- Sugar molecules/glucose/ monosaccharides Lipid- fatty acids & glycerol Protein- ( enzymes) amino acids Nucleic acid- nucleotides 24. Describe the enzyme process. (p. 52-53) • An enzyme (which is a type of protein) binds to a SPECIFIC substrate (like a puzzle piece or lock & key. It only can catalyze 1 type of substrate) • Substrate reaction produces a product • When product produced the enzyme is released to repeat. • Enzyme does not change only the substrate. 25. Describe the main function of the enzyme (it’s a type of protein). (page 51) • is a catalysts that speeds up reactions 26. What affects the reaction of an enzyme? (page 53) • Temperature, pH & concentration can affect the catalyzing of an enzyme 27.Make a Venn diagram of animal and plant cells. (pages 174-181) Plant cell • Cell wall • Chloroplasts • Brick like shape 1 large vacuole • • • Both ER Mitochondria cell membrane bound Nucleus Cytoplasm golgi ribosomes •Animal cell centrioles possibly lysosomes Varies in shape small vacuoles 28.Define semi-permeable. • also called selectively permeable refers to the cells and nuclear membranes ability to let only selected substances come in and out in an attempt to stay in homeostasis 29. Describe the function of the following organelles: (pages 174-180) Semi-permeable outer layer of cell that regulates what enters and leaves the cell • Cytoplasm- •space within cell • Nucleus •-Control center of the cell • Cell membrane- 29 Cont. •Ribosomes- makes proteins • Rough ER- -transports proteins that ribosomes make and materials throughout the cell •Golgi Body- •modifies, packages and distributes proteins 29. Cont. •Smooth ER-- makes and modifies lipids • Mitochondria- Makes energy (ATP) for the cell by breaking down glucose •Vacuole- •stores water and material for the cell •1 large one in plant—smaller ones in animals 29. Cont. Chloroplasts-Absorbs and uses sunlight in plant cells & photosynthesis occurs here Cell Wall- Outside of a plant cell that gives support & protection-gives box-like shape 30. Define and describe the passive transport methods:(p183-186) • Passive transport is the moving of molecules WITHOUT energy • from high to low concentration (crowded to not crowded areas) • The 3 types are below 30.Cont. Diffusion•High to low concentration movement of small particles through the membrane without energy facilitated diffusion High to low concentration movement of larger particles through channel proteins in the membrane without energy 30. cont. • -osmosisdiffusion of water -water moves to areas of high concentration of water molecules (low concentration of solute) to low concentration of water molecules(high concentration of solute) 30. cont • -turgor •filling of the vacuole in a plant cell high-full vacuole= •healthy plant low-empty vacuole= •wilting and plasmolysis 31. What are the 2 layers of the cell membrane made of and where are the polar heads facing and where do the nonpolar tails facing? Who likes water and who doesn’t? • Phospholipid bilayer with the polar heads facing inside and outside of the cell (loves water) and the nonpolar tails on the inside of the membrane (hates water) 32. Define and describe the active transport methods: • *Active transport requires ENERGY and goes from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration. Endocytosis and exocytosis are forms of active transport 32. Cont. • - Endocytosis- Taking of large particles or cells into the cell requires energy • -Exocytosis- •removing (exiting) of particles out of the cell requires energy