* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download BioCellsCh7through p. 180
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
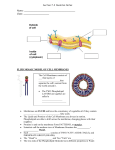
Chapter 7A View of the Cell: ARE THOSE OUR CELLS? Section 7.1 Cell: Smallest unit that can carry out all the activities necessary for life. Can survive on its own or has potential to do so Is highly organized for metabolism Senses and responds to environment Has potential to reproduce Anton Von Leeuwenhoek, the first person to observe "animalcules" through a microscope, didn’t at all like what he saw. ROBERT HOOKE— “Cells” crude compound micriscope Fig. 4.1, p. 50-51 The Cell Theory Electron Microscopes 1930’s Uses a beam of electrons to magnify to to 500,000 X Cell surfaces; internal structures CELL DIFFERENCES Size; Shape; Types and number of Internal Structures Example: muscle cells have a lot of __________________ for ATP production (high energy needs) SIMILARITIES Functionally Two Basic Cell Types 1. Prokaryotes No Nucleus No internal membrane-bound organelles Bacteria (2 Kingdoms) 2. Eukaryotes Have internal membrane –bound organelles. Other 4 kingdoms. (Animalia, Plantae, Protista, Fungi) 7.2 The Plasma Membrane Selectively permeable Water and small molecules like O2, CO2 , and nonpolar molecules --freely pass through. Charged particles (like ions) and large molecules need special assistance (proteins assist movement) -------------------------------------------Try an analogy-------------------------------------------------- . Plasma Membranes Phospholipids-Polar “head” and 2 non-polar tails Click to view animation. animation The Phospholipid Bilayer Main component of membranes Gives the membrane its fluid properties Two layers of phospholipids-end to end. Polar and Nonpolar regions A mosiac The Fluid Mosaic Model A mosaic of materials Phospholipid bilayer Proteins Cholesterol Fluid—because the phospholipids are unsaturated. Some of the proteins are free to move within the membrane too Functions of Membrane Components Cholesterol—give it some stability. Transport Proteins Help regulate entry and exit of molecules and ions. Cell Surface Markers (have sugars attached). Attached to cell surface. Like a cell’s ID tag. Class Work. May work with a partner, but each is to complete this. P. 174 Draw prokaryotic cell, label cell components, color!!! Same for the Eukaryotic cell. How do they compare in size? 7.3 Eukaryotic Cell Structure Cell Wall Inflexible barrier. Support and protection Porous—not selective The Nucleus 1.Contains DNA—directions for making proteins Chromatin-thin; non-dividing cell Chromosomes-compact, visible when cell is dividing 2. Nucleolus—this makes ribosomes. RNA forms, exits nucleus through Nuclear Pores to the Cytoplasm Nuclear Envelope Cell functions Like a candy factory Lots of Production Need to move materials inside Need to send Finished materials (candy) out to sell and waste products Movement is regulated at the perimeter gate by security, allows controlled entry and egress. HOMEWORK READ 7.3 TERMS TO KNOW Terminology in bold fontdescribe function what organisms are they found in Describe the advantage of highly folded membranes in cells. Homework 1. Compare and contrast prokaryote and eukaryote cells. 2. Why are plasma membranes describes as a “fluid mosaic”? What is the role of cholesterol in plasma membranes? CELLS ARE LIKE LITTLE CANDY FACTORIES Structure of Cells Cell membrane Function Cell Size is Limited Importance of Water in formation of Membrane Polar vs. Non-Polar Hydrogen -Bonds Cell Size is Limited In most cases, a living thing grows because it produces MORE cells An adult simply has more cells than an infant, not simply larger cells. WHY more cells, not larger cells? Remember—Membrane Function… How fast exchange occurs depends upon the SURFACE AREA of the cell BUT, how quickly food & Waste are made depends on Cell Volume Plasma Membranes 1.Phospholipids-Polar “head” and 2 non-polar tails Click to view animation. animation Phospholipid Bilayer up close and personal Main component of cell membranes Gives the membrane its fluid properties Two layers of phospholipids Cell Membrane Proteins How their structure related to their function in the membrane 2 types of CELLS EUKARYOTE VS. PROKARYOTE Differences AND Similarities