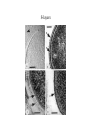
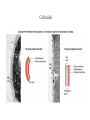
* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
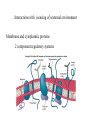
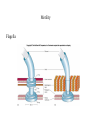
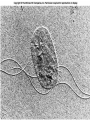
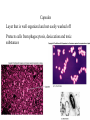
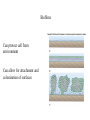
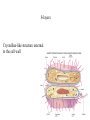
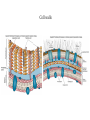
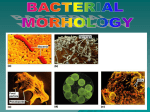
Requirements of life “ It takes a membrane to make sense out of disorder in biology….To stay alive, you have to be able to hold out against equilibrium, maintain imbalance, bank against entropy, and you can only transact this business with membranes in our kind of world.” Lewis Thomas, The Lives of a Cell Maintenance of internal environment Cell wall Mechanical stability Plasma membrane Chemical stability Metabolism Enzymes Multi-cellular organisms Organs Eukaryotic cells Organelles Prokaryotic cells Plasma membrane Interactions with (sensing of) external environment Membrane and cytoplasmic proteins 2 component regulatory systems Reproduction and inheritance of traits Chromosome (nucleoid) Reproduction and inheritance of traits Chromosome (nucleoid) Motility Flagella Motility Flagella Motility Flagella Some types of pili/fimbriae Capsules and slime layers Both are commonly made of polysaccharides Some can be made of amino acids (B. anthracis) Always contain a great deal of water Capsules Layer that is well organized and not easily washed off Protects cells from phagocytosis, desiccation and toxic substances Slime layer More loosely attached to the cell surface than a capsule Contributes to the formation of biofilms Biofilms Consist of layers of cells associated with each other through the external slime layer Biofilms Can protect cell from environment Can allow for attachment and colonization of surfaces Capsules and slime layers Production of components are tightly controlled by complex regulatory pathways S-layers Crystalline-like structure external to the cell wall S-layers Crystalline-like structure external to the cell wall Usually composed of protein subunits S-layers Adhere to the outer membrane of gram negatives and peptidoglycan of gram positives S-layers Serve to protect cells from the environment and maintain cell shape Very important in archaea lacking cell walls S-layers Cell walls Give cells shape Cell walls Give cells shape Cell walls Give cells shape Cell walls Give cells shape Protect cells from osmotic lysis Cell walls Give cells shape Protect cells from osmotic lysis May contain toxic compounds (e.g. LPS) May protect cells from toxic substances Cell walls Most bacterial cell walls contain peptidoglycan Archaeal cell walls lack peptidoglycan Some Archaea contain pseudomurein Some Archaea substitute S-layers for peptidoglycan Cell walls Cell walls