* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download answer_key_review_classification_protists_prokaryotes__fungi
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
P-type ATPase wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Protein domain wikipedia , lookup
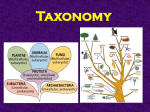
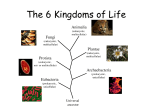
Answer Key Classification, Protists, Prokaryotes and Fungi Review Questions 1. Why do biologists assign each organism a universally accepted name? Scientific names are created so that the entire scientific community, no matter the culture and language, can understand what organism is being discussed 2. How do domains and kingdoms differ? There are only 3 domains (Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukarya), and there are 6 kingdoms (Eubacteria, Archaeabacteria, Protista, Fungi,Plantae, and Animalia). The domains are more inclusive than the kingdoms. 3. What characteristics are used to place an organism in the domain Bacteria? Prokaryotic, uniceullular, and has cell walls that contain peptidoglycan. 4. Which domain consists of prokaryotes whose cell walls lack peptidoglycan? Archaea 5. Describe the major features of the four kingdoms that comprise the domain Eukarya. (see. P.459) Protista: Eurkayotic, can be autotrophic or heterotrophic, Most are uniceullular Fungi: Eurkaryotic, cells walls of chitin, heterotrophic Plantae: Eukaryotic, cell walls of cellulose, autotrophic Animalia: Eukaryotic, no cell walls, heterotrophic 6. Create a dichotomous key for the below monsters Answers can vary.