* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CELL TRANSPORT - Oncourse : Gateway : Home
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
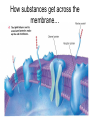
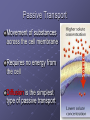
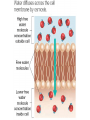
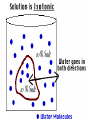
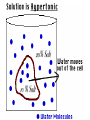
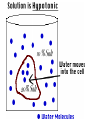
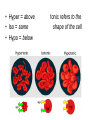
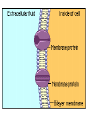
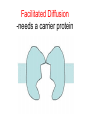
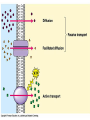
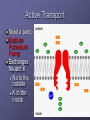
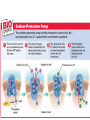
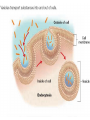
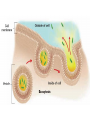
CELL TRANSPORT How substances get across the membrane… Diffusion Across Cell Membrane Semi-permeable membrane Allows only certain molecules across H2O CO2 and O2 Passive Transport Movement of substances across the cell membrane Requires no energy from the cell Diffusion is the simplest type of passive transport DIFFUSION Movement of molecules from HIGH concentration to LOW concentration Concentration Gradient - the difference between concentrations in space Simple diffusion only allows certain molecules across a membrane Eventually it will hit an equilibrium (same concentration across the gradient) OSMOSIS A type of diffusion Process by which WATER molecules diffuse across a membrane from high to low concentrations 10% Salt Solution • % solutions have to equal 100 • 10% salt (solute) would leave how much water (solvent)? • 90% water • Hyper = above • Iso = same • Hypo = below tonic refers to the shape of the cell How Cells Deal With Osmosis Animal Cells: Contractile Vacuoles Collects water and expels it from the cell How Cells Deal With Osmosis Plants: Turgor Pressure Water pressure that is exerted against cell wall Plasmolysis – loss of turgor pressure Plants wilt Cytolysis – cells burst due to hypotonic solution cell is in Facilitated Diffusion -needs a carrier protein Ion Channels • Transport ions such as Na, K, Ca and Cl • Can’t pass through membrane w/o channel Active Transport Moving molecules from a LOW concentration to a higher concentration Moving “up” their concentration gradient Requires energy from in cell ATP Active Transport Need a pump SodiumPotassium Pump Exchanges Na and K Na to the outside K to the inside Other Transport Mechanisms Endocytosis – process of ingesting macromolecules and nutrients that are too large to pass through membrane Two types: Pinocytosis Transport of other fluids Phagocytosis Transport of large particles or whole cells Phagocytes may fuse with lysosomes to destroy ingested bacteria or viruses Other Transport Mechanisms Exocytosis – process by which materials are released from the inside of the cell Release toxins and waste products Release proteins Control activity of other cells