* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CELLS - Hudson City School District
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
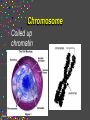
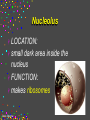
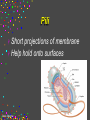
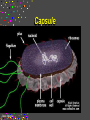
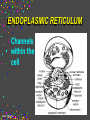
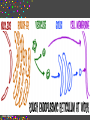
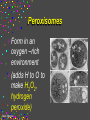
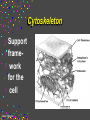
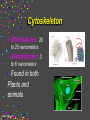
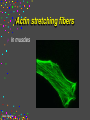
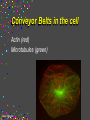
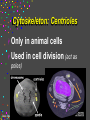
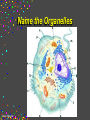
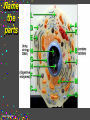
CELLS Cell Structure and Function Cinda Sheldon SIZE COMPARISONS REPRESENTS 10 MICRONS 0.5-.05 microns-VIRUS O.5-1.5 microns-BACTERIA 5 microns-RED BLOOD CELL 5-8 microns-LYMPHOCYTE 60 microns-HUMAN SPERM Cinda Sheldon CELL STRUCTURE GET OUT YOUR COLORED PENCILS Cinda Sheldon Prokaryotic Cell (bacteria) No true nucleus Cinda Sheldon Nucleoid Coiled DNA-not in a membrane Cinda Sheldon Capsule Sticky, helps the cell adhere to surfaces Cinda Sheldon Prokaryotic Here’s streptococcus, anthrax, and meningitis bacteria Cinda Sheldon Eukaryotic DO HAVE A TRUE NUCLEUS WITH A MEMBRANE – Plants – Animals – Fungi – Protists Cinda Sheldon Eukaryotic Cells Have a true nucleus bound by a membrane Cinda Sheldon EUKARYOTIC CELLS You will make an edible cell model block day – Nov. 29 + 30 Cinda Sheldon NUCLEUS Houses the genetic material: DNA Control center Cinda Sheldon The Nucleus Cinda Sheldon Nuclear Envelope-double membrane with pores to let materials in and out DNA Chromatin = DNA attached to protein as long, thin fibers Cinda Sheldon Nucleus Cinda Sheldon How Are They Related? Chromatin- Cinda Sheldon loose-made of DNA, RNA, and proteins Chromosomes -compact, tightwhen cell is going to divide Chromosome Coiled up chromatin Cinda Sheldon Nucleolus LOCATION: small dark area inside the nucleus FUNCTION: makes ribosomes Cinda Sheldon Go Bucks! We Beat Michigan! Cinda Sheldon Plasma Membrane LOCATION: Surrounds the cell FUNCTION: Sets off the cell from its environment Controls what goes in/out of the cell Cinda Sheldon PLASMA MEMBRANE Double Membrane Material Exits the Membrane Protein Channel Animation Cinda Sheldon Pili Short projections of membrane Help hold onto surfaces Cinda Sheldon Flagella Longer Projections Propel through water Cinda Sheldon Flagellum Cinda Sheldon 9 + 2 arrangement * a cylindrical array of 9 filaments * a pair of single microtubules running up through the center of the bundle Cinda Sheldon Cilia Shorter Projections Usually many of them Cinda Sheldon How do they move? Flagella and Cilia Animation (Click) Cinda Sheldon Cell Wall Protects cell helps it maintain its shape Outside the cell membrane Cinda Sheldon CELL WALL: only in plant cells + prokaryotes Cinda Sheldon Capsule Sticky outer coat Helps glue it to surfaces (like sticks, rocks, human tissue) Only in prokaryotes (bacteria) Cinda Sheldon Capsule Cinda Sheldon Cytoplasm Fluid filled region between the plasma membrane and nucleus (jello) Cinda Sheldon Organelles “little organs” most are membranous Cinda Sheldon What goes on in them? Cellular metabolism Cinda Sheldon Chemical activities of the cell What advantage is having organelles? Separate the chemicals of cellular metabolism (some may be toxic) Cinda Sheldon Increases the membrane surface area (this is where most processes occur) Ribosomes Small (21-25 nm) assemble amino acids into polypeptides (protein) Cinda Sheldon RIBOSOMES Assembles the proteins Has two subunits Cinda Sheldon Ribosome Cinda Sheldon Endomembrane System (Organelles that are formed by membranes) – endoplasmic reticulum – Golgi apparatus – lysosomes – vacuoles Cinda Sheldon ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM Channels within the cell Cinda Sheldon ER SMOOTH ER = Has no ribosomes embedded in it Makes lipids Cinda Sheldon ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM Channels to bring materials to ribosomes Assemble proteins Cinda Sheldon ROUGH ER = has ribosomes embedded in it Rough ER Cinda Sheldon Path of Proteins ER collects proteins creates a bubble around it (transport vesicle) then to cell membrane or the Golgi apparatus Cinda Sheldon Cinda Sheldon GOLGI COMPLEX (Golgi apparatus, Golgi Bodies) Sacs are not Looks like interconnected flattened stacks of pita bread Cinda Sheldon Golgi Apparatus “Molecular Repackage warehouse and finishing proteins factory” Cinda Sheldon Golgi apparatus Also known as Golgi body Golgi complex Cinda Sheldon Making A Golgi Vesicle Cinda Sheldon Vesicle Animations (Click) Vesicle Budding and Fusing vesicle animation Push the finger to the vesicle Rediscovering Biology - Unit 10 Neurobiology: Animations and Images (click on synaptic vesicles) Cinda Sheldon Golgi Bodies Making vesicles to carry out repackaged proteins Cinda Sheldon LYSOSOME Vesicles that package the enzymes that break up large molecules. “clean-up crew” Cinda Sheldon Breakin’ it Down WHAT? Food + damaged organelles + bacteria Cinda Sheldon LYSOSOMES Lysosome Animations HOW DO THEY FORM? WHAT IS THEIR JOB? Cinda Sheldon Peroxisomes Form in an oxygen –rich environment (adds H to O to make H2O2, hydrogen peroxide) Cinda Sheldon VACUOLES: Food or Water Cinda Sheldon contain water and/or storage materials Food Vacuole (b) in Amoeba Cinda Sheldon Food Vacuole Movies Phagocytosis (click) phagocytosis movie (click) Cinda Sheldon VACUOLES Vacuoles are usually larger than vesicles + lysosomes Largest structure in a plant cell Smaller in animal cells Cinda Sheldon Central Vacuole in Plants Cinda Sheldon Full and Not Full Vacuoles Cinda Sheldon Contractile Vacuole Collect water and expel it to the outside (click)Click on Contractile Vacuole of Paramecium Cinda Sheldon CHLOROPLASTS Only in plants green Cinda Sheldon CHLOROPLASTS Convert light energy to chemical energy (sugars) WHERE PHOTOSYNTHESIS TAKES PLACE Cinda Sheldon Chloroplast Granum = stack of disks where chloroplasts store energy stroma=area between grana Cinda Sheldon MITOCHONDRIA “cellular respiration” here Cinda Sheldon Note the inner folded area to increase surface area “powerhouse” (break down fuel for energy) MITOCHONDRIA “cell’s powerhouse” Cinda Sheldon Mitochondria Cinda Sheldon Combines food with oxygen to release energy (such as ATP) Mitochondrion (note folds) Cinda Sheldon Cytoskeleton Support frame work for the cell Cinda Sheldon Cytoskeleton Cinda Sheldon Cytoskeleton Microtubules 20 to 25 nanometers Microfilament to 6 nanometers Found in both Plants and animals Cinda Sheldon 3 Microtubule Cinda Sheldon Actin stretching fibers In muscles Cinda Sheldon Conveyor Belts in the cell Actin (red) Microtubules (green) Cinda Sheldon Cytoskeleton: Centrioles Only in animal cells Used in cell division (act as poles) Cinda Sheldon Centrioles Found perpendicular in pairs Cinda Sheldon Microfilaments + Tubules “cytoskeleton” Cinda Sheldon Cinda Sheldon Name the Organelles Cinda Sheldon Interactive Cells Cell Models: An Interactive Animation (click) A Typical Animal Cell - Learning Activity - Fla - Flash Player Installation (click) Cinda Sheldon Cell Junctions Structures that hold the cells together: Plant cells = plasmodesma Animal cells = extracellular matrix Cinda Sheldon “holes in the wall” Plasmodesma (plural) = Holes that allow water to pass through Cinda Sheldon Note the channels between cells Plasmodesmata (sing.) Cinda Sheldon Extracellular Matrix Some anchor, communicate with other cells, or offer leakproof covering Cinda Sheldon Name the parts Cinda Sheldon