* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cells * The building blocks of life
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
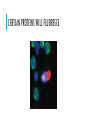
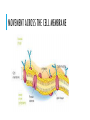
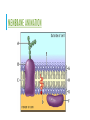
CELLS – THE BUILDING BLOCKS OF LIFE CELL THEORY – THE HISTORY BEHIND IT The cell was discovered by Robert Hooke in 1665 He looked at a piece of cork under a microscope and noted that it looked like honeycomb In 1674 Anthony van Leeuwenhoek saw the first living cells using a compound microscope CELL THEORY All living things or organisms are made of cells New cells are created by old cells dividing into two Cells are the basic building blocks of life MODERN CELL THEORY 1. The cell is the fundamental unit of structure and function in living organisms. 2. All cells arise from pre-existing cells by division. 3. Energy flow (metabolism and biochemistry) occurs within cells. 4. Cells contain hereditary information (DNA) which is passed from cell to cell during cell division. 5. MODERN CELL THEORY CONTINUED 5. All cells are basically the same in chemical composition in organisms of similar species. 6. All known living things are made up of one or more cells. 7. Some organisms are made up of only one cell and are known as unicellular organisms. 8. Others are multicellular, composed of a number of cells. 9. The activity of an organism depends on the total activity of independent cells. VIEWING CELLS – MICROSCOPY COMPOUND MICROSCOPES FLUORESCENT MICROSCOPES CERTAIN PROTEINS WILL FLUORESCE ELECTRON MICROSCOPES TYPES OF CELLS Prokaryotic – simple cells, DNA is not contained, no organelles Ex: bacteria Eukaryotic – more complex cells, DNA is contained, organelles Ex: animal cells and plant cells EUKARYOTIC CELLS - ORGANELLES CELL MEMBRANE A phospholipid layer that allows transport into and out of a cell NUCLEUS The control center for the cell Contains DNA Surrounded by a double membrane ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM Allows for transport within the cell Rough E.R – has ribosomes, makes protein Smooth E.R- has no ribosomes, makes lipids (fats) Ribosome: Site of protein sysnthesis GOLGI APPARATUS Packages, stores and delivers proteins LYSOSOMES Clean the cell and destroy worn out cell parts MITOCHONDRIA Powerhouse of the animal cell – where cellular respiration occurs CHLOROPLAST Found in plant cells only Site of photosynthesis Clorophyll gives the plant a green color CELL WALL Thick outer layer protecting plant and bacterial cells VACUOLES Storage of water, nutrients (food), waste Plants generally have one large vacuole while animal cells have several smaller vacuoles MOVEMENT ACROSS THE CELL MEMBRANE STRUCTURE OF THE MEMBRANE Made of Phosopholipids – provide a barrier from things entering and leaving the cell Fatty acids – maintains shape Proteins – serve as a gate way to allows things in and out of the cell http://www.phschool.com/science/biology_place /biocoach/biomembrane1/regions.html MEMBRANE ANIMATION DIFFUSION/OSMOSIS Movement of molecules across the membrane from high concentrations to less concentrations TERMS Isotonic – two solutions with the same concentration Hypertonic – a solution with a higher concentration than another Hypotonic – a solution with a lower concentration than another FACILITATED DIFFUSION Movement of molecules from areas of more concentration to less concentration using proteins Used with larger molecules ACTIVE TRANSPORT Movement of molecules from areas of lower concentration to higher concentration using proteins Requires energy! TERMS Endocytosis - Transport into the cell using a vesicle Phagocytosis – transport into the cell using a vesicle that is destroyed by lysosomes Exocytosis – Tr Video: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DuDmvlbpjHQansport out of the cell using a vesicle Animation: http://life9e.sinauer.com/life9e/pages/06/062003.html CELL DIVISION: MITOSIS VS MEIOSIS CANCER – WHEN CELLS GO WILD!