* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Mitosis Meiosis
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
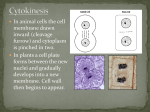
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Mitosis and Meiosis Underline the sections which relate to the diagrams you have. Mitosis • Mitosis is a type of cell division which organisms use for growth and repair or replacement of old or damaged cells. • In mitosis one cell (the mother cell) divides to form two new daughter cells. • The daughter cells are genetically identical to the mother cell. • The diploid mother cell (diploid means it has 2 sets of chromosomes) doubles its DNA so that it has one set for each new cell. This means that each daughter cell has a full set of chromosomes. Meiosis • Meiosis is the type of cell division which only occurs for the formation of sex cells (gametes) like eggs and sperm for sexual reproduction. • The mother cell is a diploid cell and the DNA replicates, as in mitosis, but following this, there are two divisions resulting in four haploid (half the number of chromosomes of a diploid cell) daughter cells. • Unlike mitosis, cells produced by meiosis are not genetically identical to the mother cell. • This means that every egg or sperm contain half the DNA needed to form a human, so that when they join together at fertilisation, they form a new diploid cell. • This then divides by mitosis to grow into a baby. Mitosis and Meiosis Arrange the diagrams in the order that you think they should go. Meiosis DNA replicates DNA replicates Mother cell Mother cell Mitosis