* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download reflex
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Neural coding wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience in space wikipedia , lookup
Biological neuron model wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Caridoid escape reaction wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Proprioception wikipedia , lookup
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
Evoked potential wikipedia , lookup
Spinal cord wikipedia , lookup
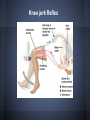
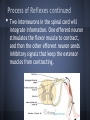
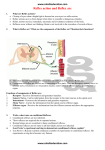
Reflexes How Reflexes Were Found • • • Sir Charles Sherrington (1857-1952) was the first to introduce the word 'reflex', taking the view that sensory information going into the cord was reflected out again along the motor nerve fibres He said that the reflection of sensory information was the equivalent to a beam of light being reflected off of a mirror. Sherrington referred to the combination of a receptor, conductor and effector as a reflex arc. How reflexes work Reflexes work when sensory neurons become interneurons in the gray matter. Afterwards the interneuron become motor neurons. Knee jerk Reflex Examples of Reflexes • • • • Blinking when something flies toward your face. Raising your arm when something is thrown at you. Coughing and sneezing Shivering Quick Videos http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wLrhYzdb bpE reflex test: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=eCrY0m5TFU Process of a Reflex • • • First a stimulus causes the receptor to stimulate the afferent neuron in the PNS. The afferent neuron then transmits an impulse to the spinal cord. The impulse will transmit through the ganglion then to the gray matter in the spinal cord. (Ganglion is a structure containing a number of nerve cell bodies). Process of Reflexes continued • Two interneurons in the spinal cord will integrate information. One efferent neuron stimulates the flexor muscle to contract, and then the other efferent neuron sends inhibitory signals that keep the extensor muscles from contracting. Types of Reflexes Cranial Reflex-A cranial reflex is a fast, involuntary response to a stimulus. It uses the brain stem as an integrating center. Spinal Reflex- A spinal reflex is a reflexive action mediated by cells in the spinal cord, bypassing the brain altogether. Types of Reflexes (cont) Somatic Reflexes- Somatic reflexes involve a response that involves a skeletal muscle contraction in response to a stimuli. Autonomic Reflexes- An autonomic reflex is one that involves the response of an organ, such as the peristaltic contraction of the smooth muscle of the intestines, that is not controlled consciously. What can go wrong!?!?!?!?! 1. Methylglutaconic Aciduria: Genetic Disorder 2. Acroosteolysis Neurogenic: Total loss 3. STNR: Symmetrical Tonic Neck Reflex 4. Moto Reflex: should disappear within 2-4 months 5. Reflex Sympathetic Dystrophy: Pain disorder Bib • • • • • • • http://www.rightdiagnosis.com/symbol/3_methylglutaconic_aciduria_ty pe_4/intro.htm http://www.encyclopedia.com/topic/reflex.aspx#1-1O128:reflexes-full http://faculty.stcc.edu/AandP/AP/AP1pages/nervssys/unit12/reflexes.h tm http://kidshealth.org/kid/talk/qa/reflexes.html http://www.wisegeek.org/what-is-a-spinal-reflex.htm http://moveplaythrive.com/Reflexes/ http://www.medicinenet.com/reflex_sympathetic_dystrophy_syndrome/ article.htm