* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Structure and Function of Cells
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
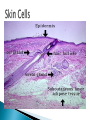
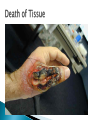
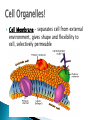
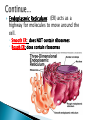
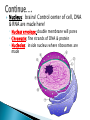
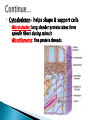
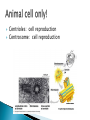
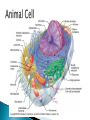
Chapter 4 Honors and Lab Biology Quick Write: ◦Why do we need to learn about cells? Healing time is radically reduced and scarring almost eliminated by bioartificial skin! Cells that do NOT contain membrane bound organelles. (unicellulat) Cells that DO contain membrane bound organelles. Cells were discovered due to microscopes in the early 17th century ROBERT HOOKE 1665 (english scientist) examined a slice of cork, he saw “little boxes” they reminded him of small rooms….cells! These were dead plant cells. ANTON VAN LEEUWENHOEK 1632-1723 (dutch microscope maker) first to observe living cells Is the smallest unit of matter that can carry out all the processes of life. Organelle: parts within a cell! 1. All living things are composed of one or more cells 2. Cells are the basic unity of structure and function in an organism 3. Cells come from the reproduction of existing cells. Matthias Schleiden (1838) botanist, all plants Theodor Schwann (1839) zoologist, all Rudolf Virchow (1855) physician, cells come are composed of cells animals are composed of cells ONLY from other cells. Not all cells are alike! They vary in… ◦ A) size ◦ B) shape ◦ C) internal organization SIZE: range from .2m – 0.2um (most are 10-50um) -not all are microscopic (most are) ex: giraffe’s nerve cells extend 6.5 ft. down it’s leg!! Cells are limited in size by the ratio between their outer surface area and their volume Organelles: parts of a cell, have specific jobs Tissues: groups of cells that have a similar function ! Organ systems- a group of organs that work together to perform a set of related tasks. Digestive system includes: the stomach, esophagus, intestines and mouth. Cells→Tissues→Organs→Organ Systems Cell Membrane – separates cell from external environment, gives shape and flexibility to cell, selectively permeable Cytoplasm: ◦ gelatin like aqueous fluid called cytosol ◦ Cytoplasmic streaming ◦ Mostly water but also salts and organic molecules Mitochondia: power house of the cell! Where cellular respiration occurs, production of ATP, has it’s own DNA ◦ Cristae: inner membrane creating many folds to increase surface area Ribosomes: where proteins are made, ◦ Free Floating Ribosome: make proteins for the cell ◦ Ribosomes attached to ER: make proteins to be exported from the cell Endoplasmic Reticulum: (ER) acts as a highway for molecules to move around the cell. ◦ Smooth ER: does NOT contain ribosomes ◦ Rough ER: does contain ribosomes Golgi Apparatus (bodies) processes, packages, and secretes a) product is assembled (moves from ER to golgi, where it is put together and adjusted) b) product is packaged (in new sacs) c) product is mailed out (sent out of cell) Cilia: short hair like projections beat together to move an organism ex: humans trachea cilia move fluids and mucus! YUM Flagella: long, whiplike projections, single or in pairs, rapid movement, ex: sperm Nucleus: brains! Control center of cell, DNA & RNA are made here! ◦ Nuclear envolope: double membrane will pores ◦ Chromatin: fine strands of DNA & protein ◦ Nucleolus: inside nucleus where ribosomes are made Lysosome: digestive enzymes, digest food, disease causing bacteria, old organelles, ex: lysosomes eat up tissue between fingers in embryos, usually only in animal cells Cytoskeleton- helps shape & support cells ◦ Microtubules: long slender protein tubes form spindle fibers during mitosis ◦ Microfilaments: fine protein threads Centrioles: cell reproduction Centrosome: cell reproduction Cell Wall: rigid covering made of cellulose, protects cell, goes OUTSIDE cell membrane Central Vacuole: huge structure which may take up 90% of the space in plant cell Plastids ◦ a) chloroplasts : site for photosynthesis ◦ b) chromoplasts: stores red and yellow pigment ◦ c) leucoplasts: non pigmented