* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Biochemical Pathways - NCEA Level 2 Biology
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of diabetes Type 2 wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Saethre–Chotzen syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Gene desert wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Fetal origins hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Tay–Sachs disease wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Gene nomenclature wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
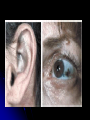
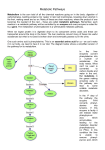
Biochemical Pathways How they are affected by mutations. Biochemical Pathways All biochemical pathways are catalysed by enzymes. The coding for these enzymes is controlled by a gene. If an organism has a faulty gene, it may not be able to make the enzyme. Biochemical Pathways This means that the biochemical pathway would stop at that point and there would be an accumulation of the chemical prior to the faulty enzyme. A Biochemical Pathway Gene 1 Gene 2 Expression of gene 1 produces enzyme 1 Enzyme 1 A Gene 3 Expression of gene 2 produces enzyme 2 Enzyme 2 B Expression of gene 3 produces enzyme 3 Enzyme 3 C D Diseases of Inborn Errors of Metabolism Phenylketonuria - PKU This is a serious disease, which if left untreated, can result in severe mental retardation. It results from a defect in the enzyme E1 that converts phenylalanine to tyrosine. This results in an accumulation of phenylalanine and other minor metabolic products in the body. Phenylketonuria - PKU People with this disease are lightly pigmented, although there is usually enough tyrosine in their diets to allow them to make melanin. All babies in NZ are tested for PKU at birth, and if it is present the children are put on a strict diet which can prevent the effects. Phenylketonuria - PKU This diet greatly reduces the amount of phenylalanine accumulated. Phenylalanine is one of the essential amino acids, which is not made by the body, so it can be controlled by diet. A small amount of phenylalanine has to be given to maintain normal growth. Albinism The most common type of Albinism is due to lack of the enzyme E3 that makes melanin from tyrosine. Because Albino people cannot make melanin, they have white hair and pink eyes, and their eyes and skin are very sensitive to sunlight. Albinism is widespread in the animal kingdom. (rats, rabbits, snakes, birds) In Humans In Other Animals Alkaptonuria This is due to lack of enzyme E4 that processes homogentisic acid. Its absence means that homogentisic acid accumulates in the tissues. People with this condition appear normal as children, but are detected when their nappies start turning black Alkaptonuria As they grow, they develop a blue-black discolouration of the ears, whites of the eyes, tips of the nose, and other areas where cartilage is just under the skin. Their urine turns black after exposure to sunlight for several hours. They often have severe arthritis, caused by accumulation of the metabolite in the cartilage of the joints. Phenylalanine Minor Metabolic Products E1 E3 Tyrosine Melanin E2 Homogentisic acid E4 Further metabolic Products E = enzyme