* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Genetics Notes - Biloxi Public Schools
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Genetically modified food wikipedia , lookup
Genetically modified crops wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
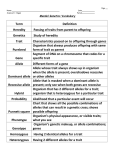
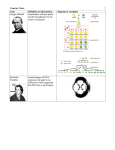
Term 3---Genetics Notes term definition or information diagram or examples Gregor Mendel experiments with pea plants laid the foundations for the science of genetics Thomas Hunt Morgan known for his experimental research with the fruit fly (Drosophila) by which he established the chromosome theory of heredity discovered that fruit fly eye color is sex-linked Rosalind Franklin created images of DNA molecules through X-ray diffraction which suggested that DNA has a spiral shape Francis Crick & James Watson developed the double-helix model of the structure of DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) The DNA molecule resembles a twisted ladder or zipper and the DNA sequence forms a code. 1 2 Term 3---Genetics Notes term trait definition or information any characteristic of an organism such as body shape or what it eats All traits are inherited. passed from parent to offspring heredity passing of traits from one generation to another during reproduction reproduction---process by which organisms make more organisms of the same kind --sexual reproduction --asexual reproduction *** some organisms can reproduce both sexually and asexually diagram or examples Term 3---Genetics Notes DNA determines what traits are (deoxyribonucleic passed from one generation to acid) the next—blueprint of an organism Before a cell divides, it makes a copy of its DNA. This ensures that both new cells have all the genetic information they need. A genome is the complete sequence of an organism’s DNA. chromosomes gene allele A molecule of DNA can be very long. To fit inside the nucleus, the DNA wraps around proteins and coils tightly. These tightly coiled structures that contain the genetic information ***genetic mutations---the permanent change in the DNA sequence that makes up a gene ---may be inherited from parents or acquired during a person’s lifetime ---acquired mutations are not passed to offspring small section of DNA on a chromosome that carries information about a trait Hundreds of genes are located on each chromosome each gene of a gene pair (different forms of a gene) 3 Term 3---Genetics Notes Punnett square used to predict the possible genes and traits of offspring, based on the genes of their parents --monohybrid cross (1 trait) --dihybrid cross (2 traits) phenotype physical characteristics of an organism or what is expressed/shows (tall, short, eye color, flower color) genotype all the genes that are passed on to an offspring or the genetic makeup of an organism—the letters on the Punnett square (tt, Tt, TT) The genotype of an organism determines its phenotype. 4 5 Term 3---Genetics Notes dominant one allele covers over or masks another allele of that trait (visible or seen) A dominant allele is expressed in the phenotype of an organism. If the organism has that allele, it will show that trait. recessive alleles are seen only when a trait is recessive pure (two recessive traits---tt) If offspring has one dominant allele and one recessive allele for a trait, the recessive trait is not expressed purebred organism is one that has two matching alleles for a trait (example: TT or tt) homozygous (homozygotes)- organisms that have two identical alleles for a particular trait (BB or bb) hybrids incomplete dominance codominance organisms that inherit two different alleles for a trait (Tt) heterozygous (heterozygotes)-- organisms that have two different alleles for a particular trait (Bb) heterozygous alleles are both expressed, resulting in a combined phenotype For example, in crosspollination experiments between red and white snapdragon plants the resulting offspring are pink. alleles of a gene pair in a heterozygote are fully expressed resulting in offspring with a phenotype that is neither dominant nor recessive R = allele for red flowers W = allele for white flowers red x white pink RR x WW 100% RW R = allele for red flowers W = allele for white flowers red x white red & white spotted RR x WW 100% RW Term 3---Genetics Notes pedigree genetic family tree The parental generation is denoted as the P1 generation. The offspring of the P1 generation are the F1 generation (first filial). The self-fertilizing F1 generation produced the F2 generation (second filial). An autosome or autosomal is a chromosome that is not a sex chromosome. 6 Term 3---Genetics Notes Biotechnology--Term Definition or information biotechnology manipulation of living things to make useful products causes changes in organisms selective breeding (artificial selection) intentional mating of organisms to produce offspring with specific traits breeding of animals or plants having desirable characteristics domesticated animals is the process of developing a cultivated breed over time weeding-out of undesired characteristics and the fixation of desired traits Cross-pollination--crosses two different varieties of vegetable but has traits of both parents 7 Diagrams or examples Term 3---Genetics Notes genetic changes the genetic engineering material of a living organism make medicines and treat disease improve crops produce organisms in scientific research Gene splicing ---a gene from one organism is inserted into the DNA of another organism Examples----- produce human insulin --- make medicine ---prevent inherited disorders disease resistance---make corn that is resistant to some herbicides (product that kills weeds) make food better tasting and last longer Gene therapy involves replacing the nonworking cells with cells that have been genetically altered. ---may negatively affect other genes. Benefits of Biotechnology make crops that are resistant to disease, herbicides, and frost crops taste better and more nutritious Stoneville Pedigreed Seed Company-to improve cotton Stoneville Pedigreed Seed Company 1st to sell genetically altered cotton plants Bacteria to help clean oil spills Risks of Biotechnology Genes bred into some crop plants may cross over into wild populations GE foods must be tested for safety; may cause allergic reactions may cause a new disease that could not be treated with available drugs harmful new organisms could escape into the environment How human gene information could be used--Ex.--an insurance company might refuse to cover a person who carries a gene for a specific disease GE crops may be too successful--If one kind of rice is more nourishing than any other, all the farmers in an area might plant that kind of rice. In the short term, everyone would benefit from the modified rice. However, the new rice might be vulnerable to disease or it might not produce a crop in a particularly wet or hot weather. If people have planted only one kind of rice, they could lose the entire crop. If farmers grow many different breeds of rice, they will not lose the whole harvest. 8 9 Term 3---Genetics Notes Disorder Symptom Cystic fibrosis Mucus clogs lungs, liver, and pancreas; victims usually don’t survive to adulthood Impaired blood circulation, organ damage ---Some scientists think that people with one mutated sickle cell gene are not affected by sickle cell anemia and have some protection against malaria Deterioration of central nervous system in infancy; death occurs in early childhood Failure of blood to clot Sickle cell anemia Tay-Sachs disease Hemophili a Muscular dystrophy Down syndrome Color blindness Wasting away of muscles; shortened life expectancy mild to moderate learning disabilities, developmental delays, characteristic facial features, and low muscle tone in early infancy person's ability to ascertain specific colors, and in some instances all colors Genetic Disorders Defect Failure of chloride ion transport mechanism Pattern of Inheritance Autosomal recessive Frequency among human births 1/2,080 (whites) Abnormal hemoglobin molecules Autosomal recessive 1/500 (African Americans) Defective form of enzyme hexosaminidase A Autosomal recessive 1/1,600 (Jews of European descent) Defective form of bloodclotting factor Muscle fibers degenerate X-linked recessive X-linked recessive 1/7,000 Genes on an extra copy of chromosome 21 malfunctions of the retina, the inner eye lining 1/10,000 1/800 X-linked recessive 1/33,000 in U.S.