* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download REVIEW of CELL PARTS AND FUNCTION:
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
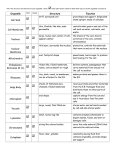
REVIEW of CELL PARTS AND FUNCTION: CELL MEMBRANE…..boundary setting structure that retains the contents of the cell; serves as a selectively permeable barrier to the environment and regulates the movement of materials into and out of the cell. NUCLEAR MEMBRANE: the double membrane that encloses the nucleus of the cell. Regulates movement of materials into and out of the nucleus. CENTRIOLES: a cylindrical organelle of animal cells and some lower plants which contains microtubules in a characteristic "9 + 2" pattern. The exact role of the centriole in the formation of the spindle during cell division is not known. MITOCHONDRIA: site of aerobic respiration in eukaryotic cells it is a membrane bound organelle found in greater numbers in cells with high energy demands such as muscle. Made up of internal folds called cristae it is a double membraned organelle. RIBOSOMES: site of protein synthesis, these may be found as part of the rough endoplasmic reticulum. ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM: granular and agranular, it is the system of internal membranes within the cell. Rough has ribosomes in conjunction with it. Smooth does not. Smooth serves in the synthesis of lipids, carbohydrate metabolism and the detoxification of drugs and poisons. The rough is responsible for moving the proteins secreted by the to the golgi apparatus. GOLGI APPARATUS: composed of flattened sacked membranes, each stack is called a dictysome, it repackages proteins, carbohydrates are added here to form glycoproteins. Glycoproteins form salivary, intestinal, and respiratory tract secretions. They are also important components of hormones, enzymes and connective tissues. LYSOSOME: organelle which contains powerful digestive enzymes which are sometimes used in "cell suicide". When energy flow to the membrane from the mitochondria is interrupted, the lysosome membrane ruptures releasing its contents resulting in the destruction of the cell. Found in protozoans, sperm and egg, thyroid cells, and leukocytes. MICROTUBULES: thick fibers found inside the cell they are composed of globular protein- tubulin, and make up the centrioles, cilia, and flagella. MICROFILAMENTS: thin fibers found in the cell these are required for muscular contraction and microvilli formation. These give the cell shape and fix the organelles of the cell. CHLOROPLASTS: found in plant cells, these are membrane bound organelles which contain the pigment chlorophyll. Site of photosynthesis, it is made up of grana (penny like stacks), thylakoids, and stroma NUCLEUS: bound by a double membrane, contains the genetic material of the cell. Controls the growth and reproduction of the cell. NUCLEOLUS: a small spherical body found within the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell, it is the site of synthesis of ribosomal RNA. CYTOPLASM: the living contents of the cell excluding the nucleus. KNOW THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN A PLANT AND AN ANIMAL CELL. 1. Plant cells have a single large water vacuole. 2. Plant cells have chloroplasts. 3. Plant cells have cell walls and cell membranes. 4. Plant cells undergo cleavage plate cytokinesis and animal cells undergo cleavage furrow cytokinesis. 5. Animal cells have centrioles, and plant cells do not. http://www.mrsbennett.com/html/cell_parts_and_funtion.html