* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Memory - Hensley
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Source amnesia wikipedia , lookup
Autobiographical memory wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive memory wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Eyewitness memory wikipedia , lookup
Exceptional memory wikipedia , lookup
Multiple trace theory wikipedia , lookup
Memory consolidation wikipedia , lookup
Music-related memory wikipedia , lookup
State-dependent memory wikipedia , lookup
Atkinson–Shiffrin memory model wikipedia , lookup
Childhood memory wikipedia , lookup
De novo protein synthesis theory of memory formation wikipedia , lookup
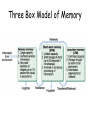
Self-Defining Memories • “The memories you have of your life experiences are what truly make you unique.” (central to your identity) • Do you agree with the statement? Why or why not? • According to Jefferson Singer’s research, self-defining memories always retain 5 qualities: • • • • • Emotional Intensity: take hold of our feelings both positive and negative Vividness: have intensity and clarity that highlights what matter most to us Repetition: on average they recur between once a week and once a month Connections to similar memories: tend to be part of a script (series of memories that tend to overlap in their plot & major themes) Lasting goals and unresolved conflicts: alert us to what matters most in our lives Fact or Falsehood? 1. Memory storage is never automatic; it always takes effort. 2. The day after you are introduced to a number of new students, you will more easily recall the names of those you met first. 3. Memory aids are no more useful than simple rehearsal of information. 4. Only a few people have any type of photographic memory. 5. Although our capacity for storing information is large, we are still limited in the number of permanent memories we can form. 6. We store information in memory as libraries store their books, that is, in discrete precise locations. 7. When people learn something while intoxicated, they recall it best when they are again intoxicated. 8. The hour before sleep is good time to commit information to memory. 9. Repeatedly imagining a nonexistent event can lead us to believe it actually happened. 10. Children typically will repress any memory of having seen one of their parents being murdered . Memory The persistence of learning over time through the storage and retrieval of information. Take out a piece of paper….. • Name the seven dwarves….. Now name them….. Was it easy or hard? • It depends on several things…. • If you like Disney movies? • When was the last time you have seen the movie? • Are people around you being a loud pain so you cannot concentrate? Recall Versus Recognition Recall • you must retrieve the information from your memory • fill-in-the blank or essay tests Recognition • you must identify the target from possible targets • multiple-choice tests The Memory Process Three step process…. 1. Encoding: The processing of information into the memory system. 2. Storage: The retention of encoded material over time. 3. Retrieval: The process of getting the information out of memory storage. Three Box Model of Memory Sensory Memory • A split second holding tank for ALL sensory information. • Sperling’s research on Iconic Memory (momentary memory of visual stimuli) • Echoic Memory (auditory stimuli) Short Term Memory • The stuff we encode from the sensory goes to STM. • Events are encoded visually, acoustically or semantically. • Holds about 7 (plus or minus 2) items for about 20 seconds. • We recall digits better than letters. Short Term Memory Activity Ways to remember things in STM…so they go to LTM • Chunking: Organizing items into familiar, manageable units. • Mnemonic devices • Rehearsal Long Term Memory • Unlimited storehouse of information. • Explicit (declarative) memories-conscious memories, have to put effort in to remember • Implicit (nondeclarative) memoriesunintentional memories we might not realize we have. Explicit Memories • Episodic Memories – Specific events, episodes of your life • Semantic Memories – General knowledge Implicit Memories • Procedural Memories – Skills & how to perform them (riding a bike) • Conditioned Memories Take out a piece of paper and name all the Presidents… Encoding Information • Primacy Effect • Recency Effect • Serial Positioning Effect Spacing Effect • DO NOT CRAM!!!!!!!!!!!! • Ebbinghaus’s Forgetting Curve Course of forgetting is initially rapid, then levels off with time (e.g. you may forget what you learned in your history class 3 years ago however, what you remember now, you will probably still remember 25 or more years later. Encoding Exercise The Ways we can encode… • Visual Encoding: the encoding of picture images. • Acoustic Encoding: the encoding of sound, especially the sounds of words. • Semantic Encoding: the encoding of meaning. The Context Matters!!! • Flashbulb Memories • Mood Congruent Memory • State Dependent Memory • • • • Constructive Memory Memories are not always what they seem. Elizabeth Loftus A constructed memory is a created memory. Misinformation effect • Clip: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=PB2OegI6wvI • Assignment: Take notes on Loftus’ discussion. What does she suggest about our memories? What does her research indicate? Do you support her findings? Why or why not. Forgetting: Which is the accurate penny? Forgetting Getting a new bus number and forgetting old bus number. • Retroactive Interference: new information blocks out old information. • Proactive Interference: old information blocks out new information. Calling your new girlfriend by old girlfriends name. Storing Memories Long Term-Potentiation • long-lasting enhancement in signal transmission between two neurons that results from stimulating them synchronously. • In other words…they learn to fire together and get better at it…creating a memory.