* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download This is Most of an Old Exam
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical cascade wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Lactate dehydrogenase wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
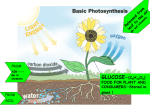
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Metabolic network modelling wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Blood sugar level wikipedia , lookup
Glyceroneogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
This is Most of an Old Exam. Please do NOT study just from this exam. Do the questions at the back of chapters too!!!!! Name General Physiology Write the letter of the best answer in the space provided at the left. There is only one correct answer for each question (5 points each). _____ 1.Which of the following statements regarding metabolic processes is FALSE? A. Cellular oxidation of food fuels is the immediate source of electrons for oxidative phosphorylation. B. In oxidative phosphorylation, both the electron transport proteins and the ATP synthase molecules are in the same membrane. C. NAD+ and FAD+ are hydrogen carrier molecules. NAD+ can carry one hydrogen and electron, FAD+ can carry two. D. Hexokinase, the enzyme that catalyzes the first reaction in glycolysis, is highly regulated via allosteric mechanisms. _____ 2.Synthesis of glucose from non-carbohydrate precursors is called gluconeogenesis. Gluconeogenesis A. is activated when blood glucose is low and an organisms glucose supplies are limited. B. uses glycogen as a source of new glucose molecules to maintain blood glucose. C. can make new glucose molecules from the direct reversal of the glycolytic pathway. D. is only activated when adipose depots of triglycerides are low. Write brief, but complete to questions 1-3. Then choose two questions from question 4-7, and write your answers (12 points each). 1. You are examining the activity of enzymes in hummingbird flight muscles. You perform specific spectrophotometric analyses for lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), citrate synthase (CS) and hydroxyacyldehydrogenase (HAD). The raw data from your analyses is shown below. Assume that in each assay you used an equivalent amount of muscle protein. Do the activities of these enzymes meet your expectations for hummingbird flight muscle? Why or why not? Explain your answer in terms of metabolic pathways and their regulation.. Time (min) 0 0.5 LDH 2.011 1.875 Absorbance CS 1.887 1.743 HAD 1.898 1.884 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0 1.486 1.186 0.975 0.795 0.555 1.623 1.515 1.235 1.003 0.798 1.796 1.794 1.795 1.796 1.797 3. We are indirectly examining the metabolic pathways and fuels used by a marathon runner. We do this by measuring changes in O2 breathed in vs. breathed out, and the changes in CO2 breathed out. The following figure describes the results of our measurements over the course of the marathon. What kind of metabolism is probably taking place during the first 60 min of the marathon? What is the main fuel being used? Why can you say this? What kind of metabolism is probably taking place following 60 min of running? What fuel(s) is (are) being used? Why can you say this? CO2 exhaled O2 consumed 0.5 1.0 1.5 time (hours) Answer 2 of the following four questions. Use no more than half a page for each answer and be sure to indicate which questions are being answered. 4. There are at least two gradients important in the process of oxidative phosphorylation. What are two of the gradients and why are they important to the production of ATP? 5. How many molecules of O2 will be consumed during the oxidation of 1 molecule of palmitate (a 16-carbon fatty acid)? Explain how you get your answer. 6. What are the two main functions of he proteins of the electron transport chain? How are these two functions related to one another? 7. Given what you know about how enzymes are regulated, explain which enzymes you think might be highly regulated in glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and the cycle for oxidation of fatty acids. Explain your choices and speculate what might be a regulator for each enzyme you choose.