* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Sources of hydride ion
Enantioselective synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Discodermolide wikipedia , lookup
Cracking (chemistry) wikipedia , lookup
Hydroformylation wikipedia , lookup
Marcus theory wikipedia , lookup
Stille reaction wikipedia , lookup
Asymmetric induction wikipedia , lookup
Diels–Alder reaction wikipedia , lookup
Elias James Corey wikipedia , lookup
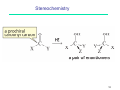
Petasis reaction wikipedia , lookup
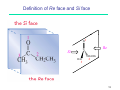
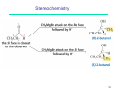
Ring-closing metathesis wikipedia , lookup
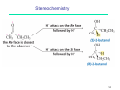
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Wolff rearrangement wikipedia , lookup
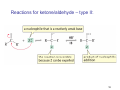
Ene reaction wikipedia , lookup
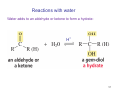
Strychnine total synthesis wikipedia , lookup
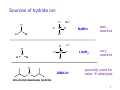
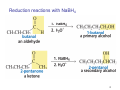
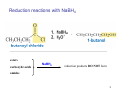
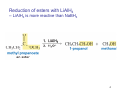
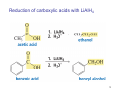
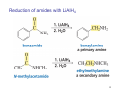
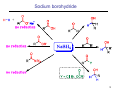
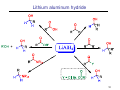
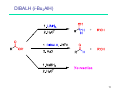
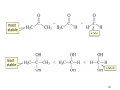
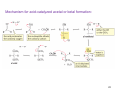
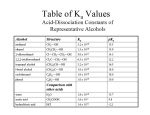
Sources of hydride ion H Na+ H H B H B H H NaBH4 less reactive LiAlH4 very reactive H H Li+ H H Al H Al H H H H Al D DIBALH specially i ll used d ffor ester aldehyde diisob t lal min m hydride diisobutylaluminum h dride 1 Reduction reactions with h NaBH4 2 Reduction reactions with h NaBH4 esters carboxylic acids NaBH4 reduction products DO NOT form amides 3 Reduction of esters with h LiAlH4 -- LiAlH4 is more reactive th han NaBH4 4 Reduction of carboxylic acids with LiAlH4 5 Reduction of amides witth th LiAlH4 6 7 Reduction of esters with h DIBALH -- DIBALH is less reactive than LiAlH4 8 Sodium borrohydride 9 Lithium alum minum hydride 10 DIBALH (i-Bu2AlH) 11 Stereochem mistry 12 Definition of Re fa ace and Si face 1 O Re C Si CH2CH3 H3C 2 3 13 Stereochem mistry 14 Stereochem mistry 15 Reactions for ketone/alldehyde ldehyde – type II: 16 Reactions wiith water Water adds to an aldehyde or kettone to form a hydrate: H+ 17 Mechanism for acid-cata alyzed y hydrate y formation 18 19 20 Reactions wiith ith alcohols 21 Mechanism for acid-catalyzed ace etal or ketal formation: etal 22 Formation of cyclic y c ketals and acetals -- act as protecting g groups 23 Why yp protecting gg gro oups? p Utilization of protecting groups g in synthesis: 24 Protecting gg groups p 25 Protecting gg groups p 26 Reactions wiith ith thiols Hg2+ Hg2+ 27 Desulfurization replace p es the C-S bonds with C-H bonds 28 Reactions of ketones/alde ehydes with primary amines ehydes 29 Reactions of ketones/alde ehydes with 2o amines ehydes 30