* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Basic Structure of a Cell
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
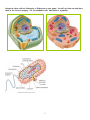
Name: ____________________________ Date: _______________ Period: ______ Basic Structure of a Cell ppt questions 59 History & the Cell Theory 1. Robert ____________ was first to view and draw ____________ cells from plants in _________. Where these cells living? _________ What was their shape? ___________ What did he call them? _____________ 3. ________________ was the first to view living cells in _________. With a _____________ microscope. . State the 3 parts of the cell theory as developed by Schleiden, Schwann, and Virchow 1. Scheiden ________ come from cells, Schwann __________ come from cells, Virchow ______ come from _______. So the theory is. a. ________________________________________________________________________ b. ________________________________________________________________________ c. ________________________________________________________________________ Discoveries Since the Cell Theory 4. a. In 1970, what did Lynn Margulis conclude about cells? What was her evidence ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ 5. . What 2 DNA-containing organelles support Margulis theory of ENDOSYMBIOSIS? _________________________ and __________________________ (Both use asexual reproduction usually seen in bacteria known as ____________ _____________.) 6. ______________, ______________, and ______________ are three basic types of cells. 7. What is the difference between unicellular and multicellular organisms? 8. What is another name for cell specialization? ___________________________ Two types of Cells Prokaryotes Definition Basic Structures Examples, Kingdoms - 1 Eukaryotes Categorize these cells as Prokaryote or Eukaryote on your paper. You will cut them out and place them in the correct category. For the unlabeled cells, add labels to organelles 2 Organelles ISN 61 1. ____________ are very small and they perform _________ functions for a cell. They are found in the ___________, and they can be ________ - ________ or not 2. The cell or __________ membrane is made of a double layer of _________________ and _____________. The cell membrane surrounds _____ cells and controls what _______ or ________ the _________. A phospholipid contains ________ and ________. The ________ is hydrophilic and the _________ are hydrophobic. In plants, it lies immediately against the _____ _______. 3. The ______ _________ is found in _________, ___________, and ___________. The cell walls in plants contain ___________, bacteria contain _____________, and fungi ____________. It’s function is to ___________ and _____________ the cell. 4. The __________ of a cell that is __________ - _________ and provides a medium for __________ ___________ to occur. This is where _____________ are suspended. 5. The __________ controls the ________ ___________ of the cell. It contains _______ and is bound by a __________ _____________. This is usually the _________ organelle. The __________ __________ is a _________ membrane, and contains nuclear ________ for materials to enter and leave. It is connected to the ____________ E.R. DNA is in the form of _____________ which is uncondensed or ____________ which is condensed for cell division. 6. The nucleolus is located in the _____________. Its main function is to __________ ____________. During cell division the ____________ _____________. 7. The ____________ helps maintain _______ shape and __________ to move around. It contains _______________ made of actin and ________________ made of ____________. 8. ____________ are found in animal cells, are ______ structures, and are made of ____________. The appear during _________ division and help to pull apart _____________ pairs to opposite poles. 9. __________________ are the powerhouse of the cell, ant their function is to make __________ in the form of ________. Plants and animals have ___________, and they are the cite of cellular _____________. They have a _________ membrane and their own _______. Inner folds are ______. What polysaccharide does the mitochondria break down to release ATP? _____________________ 10. The E.R. or, ______________ _______________, is a network of hollow __________ _________ that connect the ____________ ____________ to the cell membrane. They function in the ________ of proteins, lipids, etc… and the __________ of these products. Rough ________ has __________ that make proteins. The smooth ________ lacks _____________ and makes lipids. 11. Ribosomes are made of _______ and __________ and function as ______________ factories. They join ________ __________ together during _________ ___________ using _________ bonds. They can be attached to _________ ________ or __________ in the cytoplasm. 12. The ____________ apparatus or _________, looks like a stack of ___________ and its’ function is to ___________, _________, and _____________ molecules for storage or _____________. They use ___________ to transport materials. 13. _____________ contain __________ ____________ to break down food, bacteria, etc… Sometimes perform autolysis which is _______ ________, and they recycle _______ parts. 14. ________, which are shorter, and __________, which are longer and whip-like, aid in __________ of cells, fluids, or small particles. 15. ______________ are fluid-filled sacs for ______________. Plants have a large _________ __________. _________ vacuole found in ___________, a Protista, pumps out water to prevent lysis. 16. ____________ are found in producers ( plants or protists), uses _______ from sun to make ___________. Like mitochondria they have a ___________ membrane and their own _________. They contain Thylakoid stacks. It is the site of _____________________________ 3