* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PowerPoint slides
German Climate Action Plan 2050 wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in the Arctic wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on humans wikipedia , lookup
Climate sensitivity wikipedia , lookup
Media coverage of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Iron fertilization wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on human health wikipedia , lookup
Climate governance wikipedia , lookup
General circulation model wikipedia , lookup
Instrumental temperature record wikipedia , lookup
Climate-friendly gardening wikipedia , lookup
Climate engineering wikipedia , lookup
2009 United Nations Climate Change Conference wikipedia , lookup
Global warming controversy wikipedia , lookup
Economics of climate change mitigation wikipedia , lookup
Fred Singer wikipedia , lookup
Economics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Attribution of recent climate change wikipedia , lookup
Climate change mitigation wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Scientific opinion on climate change wikipedia , lookup
Climate change, industry and society wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and poverty wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in New Zealand wikipedia , lookup
Reforestation wikipedia , lookup
Surveys of scientists' views on climate change wikipedia , lookup
United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change wikipedia , lookup
Citizens' Climate Lobby wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on Australia wikipedia , lookup
Global warming hiatus wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Solar radiation management wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbon economy wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in Canada wikipedia , lookup
Public opinion on global warming wikipedia , lookup
Global warming wikipedia , lookup
Carbon governance in England wikipedia , lookup
Physical impacts of climate change wikipedia , lookup
Mitigation of global warming in Australia wikipedia , lookup
Carbon Pollution Reduction Scheme wikipedia , lookup
Politics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
IPCC Fourth Assessment Report wikipedia , lookup
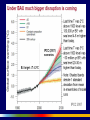
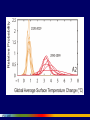
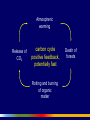
Uncertainty, Lags, and Nonlinearity: Challenges to Governance in a Turbulent World Thomas Homer-Dixon CIGI Chair of Global Systems Balsillie School of International Affairs Waterloo,Canada May 7 2009 UNCERTAINTY LAGS NONLINEARITY OPENNESS UNCERTAINTY LAGS NONLINEARITY OPENNESS UNCERTAINTY LAGS NONLINEARITY OPENNESS We need to shift from seeing the world as composed mainly of MACHINES to seeing it as composed mainly of COMPLEX SYSTEMS Whereas MACHINES • can be taken apart, analyzed, and fully understood (they are no more than the sum of their parts) • exhibit “normal” or equilibrium patterns of behavior • show proportionality of cause and effect, and • can be managed because their behavior predictable . . . COMPLEX SYTEMS • are more than the sum of their parts (they have emergent properties) • can flip from one pattern of behavior to another (they have multiple equilibriums) • show disproportionality of cause and effect (their behavior is often nonlinear, because of feedbacks and synergies), and • cannot be easily managed because their behavior is often unpredictable. We’re moving from a world of RISK to a world of UNCERTAINTY (unknown unknowns) So, we must move from “management” to Complex Adaptation Battisti and Naylor, “Historical warnings of future food insecurity with unprecedented seasonal heat.” Science (9 January 2009): 240-44 Battisti and Naylor, “Historical warnings of future food insecurity with unprecedented seasonal heat.” Science (9 January 2009): 240-44 IPCC 2007 UNCERTAINTY LAGS NONLINEARITY OPENNESS LAGS • Between emission and climate response • Between cuts to emissions and reduction of warming • Between policy decision to change energy infrastructure and completion of this change “ [We show] that to hold climate constant at a given global temperature requires near zero future carbon emissions. . . . As a consequence, any future anthropogenic emissions will commit the climate system to warming that is essentially irreversible on centennial timescales.” Matthews, H. D., and K. Caldeira (2008), “Stabilizing climate requires near-zero emissions,” Geophys. Res. Lett. “[The] climate change that takes place due to increases in carbon dioxide concentration is largely irreversible for 1,000 years after emissions stop. Following cessation of emissions, removal of atmospheric carbon dioxide decreases radiative forcing, but is largely compensated by slower loss of heat to the ocean, so that atmospheric temperatures do not drop significantly for at least 1,000 years. Among illustrative irreversible impacts that should be expected if atmospheric carbon dioxide concentrations increase from current levels near 385 parts per million by volume (ppmv) to a peak of 450–600 ppmv over the coming century are dry-season rainfall reductions in several regions comparable to those of the ‘‘dust bowl’’ era and inexorable sea level rise.” Solomon et al, “Irreversible climate change due to carbon dioxide emissions,” PNAS (February 10 2009). Hansen, Atmos. Chem. Phys. 7 (2007): 2287-2312. UNCERTAINTY LAGS NONLINEARITY OPENNESS 0.25 Ice Accumulation Rate (meters per year) 0.2 0.15 0.1 0.05 0 13000 12500 12000 11500 Years before Present 11000 10500 More rapid warming at poles One reason: Ice-albedo feedback Atmospheric warming radiative Increased ocean positive feedback, absorption of sun’s energy fast Lower reflectivity of ocean surface Melting of ice 2008 4.52 mK2 Jakobshavn Ice Stream in Greenland Discharge from major Greenland ice streams is accelerating markedly. Source: Prof. Konrad Steffen, Univ. of Colorado Atmospheric warming Release of CO2 carbon cycle positive feedback, potentially fast Rotting and burning of organic matter Death of forests Atmospheric warming carbon cycle positive feedback, slow Increased airborne fraction Decreased efficiency of carbon sinks Declining efficiency of the ocean sink • Up to 30 percent decrease in the efficiency of the Southern Ocean sink over the last 20 years • Strengthening of the winds around Antarctica increases exposure of carbon-rich deep waters • Strengthening of the winds due to global warming and the ozone hole Le Quéré et al. 2007, Science Atmospheric warming Release of CH4 and CO2 carbon cycle positive feedback, potentially fast Rotting of organic matter Melting of permafrost