CDP`s 2016 Climate Change Scoring Methodology
... Please provide details of your products and/or services that you classify as low carbon products or that enable a third party to avoid GHG emissions Did you have emissions reduction initiatives that were active within the reporting year (this can include those in the planning and/or implementation p ...
... Please provide details of your products and/or services that you classify as low carbon products or that enable a third party to avoid GHG emissions Did you have emissions reduction initiatives that were active within the reporting year (this can include those in the planning and/or implementation p ...
Reducing Emissions from Deforestation and Forest Degradation
... and facilitating neutral and independent dialogues and assessments, in our view was the ideal facilitator of this process. The Institute has assembled a high-quality, diverse, and independent group of experts to provide pragmatic, fact-based analysis and assessments of a set of proposed options for ...
... and facilitating neutral and independent dialogues and assessments, in our view was the ideal facilitator of this process. The Institute has assembled a high-quality, diverse, and independent group of experts to provide pragmatic, fact-based analysis and assessments of a set of proposed options for ...
Peatlands and Climate Change
... widely studied and debated in media, but also within a scientific audience and peatland experts during recent years. Controversial opinions have been put and different parties and experts have emphasised their points of view with the latest research data, historical evidence and statistics. It seems ...
... widely studied and debated in media, but also within a scientific audience and peatland experts during recent years. Controversial opinions have been put and different parties and experts have emphasised their points of view with the latest research data, historical evidence and statistics. It seems ...
reducing australia`s greenhouse gas emissions— targets and
... expertise. These contributions have enhanced the quality of the Review and provided evidence to inform the Authority’s recommendations. A number of government departments and public agencies have supported the work of the Authority during the course of the Review. They include: the Department of the ...
... expertise. These contributions have enhanced the quality of the Review and provided evidence to inform the Authority’s recommendations. A number of government departments and public agencies have supported the work of the Authority during the course of the Review. They include: the Department of the ...
Free version - Derek Lemoine
... optimal policy under Bayesian learning. Optimality means that resources within and across periods are distributed to maximize the expected stream of global welfare from economic consumption over time under different risk states. The optimal policy must anticipate all possible thresholds, interaction ...
... optimal policy under Bayesian learning. Optimality means that resources within and across periods are distributed to maximize the expected stream of global welfare from economic consumption over time under different risk states. The optimal policy must anticipate all possible thresholds, interaction ...
Technical Reference Guide for World Climate Negotiations Model
... The purpose of the C-ROADS (Climate-Rapid Overview and Decision Support) simulator is to improve public and decision-maker understanding of the long-term implications of possible greenhouse gas emissions futures by allowing access to a rigorous – but rapid and user-friendly – computer simulation of ...
... The purpose of the C-ROADS (Climate-Rapid Overview and Decision Support) simulator is to improve public and decision-maker understanding of the long-term implications of possible greenhouse gas emissions futures by allowing access to a rigorous – but rapid and user-friendly – computer simulation of ...
FINAL Amazon Scorecard
... Climate Counts ranked six companies that fall within the Food Services sector: Starbucks, McDonald’s, Yum! Brands, Burger King, Darden Restaurants and Wendy’s International. Starbucks, the only coffee company included in the scorecard’s Food Services sector, earned 46 points on the 100-point scale f ...
... Climate Counts ranked six companies that fall within the Food Services sector: Starbucks, McDonald’s, Yum! Brands, Burger King, Darden Restaurants and Wendy’s International. Starbucks, the only coffee company included in the scorecard’s Food Services sector, earned 46 points on the 100-point scale f ...
Exploring comparable post-2012 reduction efforts for Annex I
... EU Heads of State and Government agreed in March 2007 that the EU will reduce its greenhouse gas emissions to 30% below 1990 levels by 2020 within a global and comprehensive post-2012 climate agreement. This commitment is provided that other developed countries commit to comparable reductions. Withi ...
... EU Heads of State and Government agreed in March 2007 that the EU will reduce its greenhouse gas emissions to 30% below 1990 levels by 2020 within a global and comprehensive post-2012 climate agreement. This commitment is provided that other developed countries commit to comparable reductions. Withi ...
Carbon Implications of Fuels Reduction and Ecological Restoration
... is not a disturbance to which western dry forests are adapted, and it can threaten human safety and property. Concerns about ecological integrity and fire damage have spurred substantial interest in reversing the densification that has occurred over the past century. Such management often takes the ...
... is not a disturbance to which western dry forests are adapted, and it can threaten human safety and property. Concerns about ecological integrity and fire damage have spurred substantial interest in reversing the densification that has occurred over the past century. Such management often takes the ...
THE GARNAUT CLIMATE CHANGE REvIEW
... Victorian Department of Premier and Cabinet, it included members from the public services of Queensland, Western Australia and South Australia. A secretariat office within the federal Department of Climate Change was set up in January 2008. As part of its research and analysis, the Review consulted ...
... Victorian Department of Premier and Cabinet, it included members from the public services of Queensland, Western Australia and South Australia. A secretariat office within the federal Department of Climate Change was set up in January 2008. As part of its research and analysis, the Review consulted ...
Canada`s Sixth National Report on Climate Change 2014
... Addressing short-lived climate pollutants (SLCPs) is also part of the Government of Canada’s comprehensive climate change plan. Since the last National Communication, Canada became a founding member and large financial contributor to the Climate and Clean Air Coalition to Reduce Short-Lived Climate ...
... Addressing short-lived climate pollutants (SLCPs) is also part of the Government of Canada’s comprehensive climate change plan. Since the last National Communication, Canada became a founding member and large financial contributor to the Climate and Clean Air Coalition to Reduce Short-Lived Climate ...
Holistic management
... up by scientific evidence.The aim of this study is to review some of the scientific support for the claimed effects of holistic grazing and management. There are relatively few (11) peer-reviewed studies on the effects of holistic grazing that are ‘approved’ by the Savory Institute, i.e., included i ...
... up by scientific evidence.The aim of this study is to review some of the scientific support for the claimed effects of holistic grazing and management. There are relatively few (11) peer-reviewed studies on the effects of holistic grazing that are ‘approved’ by the Savory Institute, i.e., included i ...
a call to action - CDM Policy Dialogue
... mitigate emissions in nationally appropriate ways. Favourable experiences with the CDM have enabled Brazil, China, Mexico, South Korea, and other major emerging nations to explore domestic carbon market systems. Although the CDM has been criticized for approving some projects with questionable envir ...
... mitigate emissions in nationally appropriate ways. Favourable experiences with the CDM have enabled Brazil, China, Mexico, South Korea, and other major emerging nations to explore domestic carbon market systems. Although the CDM has been criticized for approving some projects with questionable envir ...
Learning tool on Nationally Appropriate Mitigation Actions in agriculture, forestry and other land use sector
... Actions to reduce emissions and remove GHGs in the AFOLU sector provide valuable opportunities to build on and increase synergies with activities related to sustainable intensification, improved farm efficiency, climate change adaptation, food security and rural development (Module 1). NAMAs are a f ...
... Actions to reduce emissions and remove GHGs in the AFOLU sector provide valuable opportunities to build on and increase synergies with activities related to sustainable intensification, improved farm efficiency, climate change adaptation, food security and rural development (Module 1). NAMAs are a f ...
CGE training material
... Baseline Scenario Definitions: Examples from the Literature • International Energy Agency’s widely cited World Energy Outlook 2011 presents two: − Current Policies Scenario (“show how the future might look on the basis of the perpetuation, without change, of the government policies and measures that ...
... Baseline Scenario Definitions: Examples from the Literature • International Energy Agency’s widely cited World Energy Outlook 2011 presents two: − Current Policies Scenario (“show how the future might look on the basis of the perpetuation, without change, of the government policies and measures that ...
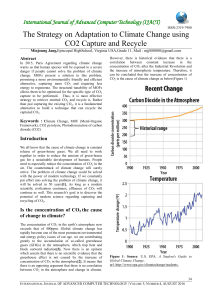
The Strategy on Adaptation to Climate Change using CO2 Capture
... benefits of design in crystalline solid-state frameworks[5]. Thus, we need a structural substance that can connect multiple of MOF. That’s where CNT (carbon nano tube) comes in handy. CNTs are efficient CO2 adsorbents and possess potential applications for CO2 ...
... benefits of design in crystalline solid-state frameworks[5]. Thus, we need a structural substance that can connect multiple of MOF. That’s where CNT (carbon nano tube) comes in handy. CNTs are efficient CO2 adsorbents and possess potential applications for CO2 ...
Climate change - Citizens` Climate Lobby
... facts simply a result of all the lobbying and campaign financing by wealthy corporations that believe climate action isn’t in their own narrow interests? For once, Congress needs to put aside its cor ...
... facts simply a result of all the lobbying and campaign financing by wealthy corporations that believe climate action isn’t in their own narrow interests? For once, Congress needs to put aside its cor ...
Low-Carbon Green Growth in Asia: Policies and practices
... Shares of Employment by Broad Sector Projections of Employment Effects of the Republic of Korea’s Green Fiscal Stimulus The Leading Countries for Green Inventions according to Patent Data Low-Carbon Policies in Asia ...
... Shares of Employment by Broad Sector Projections of Employment Effects of the Republic of Korea’s Green Fiscal Stimulus The Leading Countries for Green Inventions according to Patent Data Low-Carbon Policies in Asia ...
Finland`s Fifth National Communication under the
... 6.2.3 Impacts on nature and natural resources, and the related adaptation measures . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 163 6.2.4 Impacts on industries, infrastructure and human well-being, and the related adaptation measures . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 177 6.2.5 I ...
... 6.2.3 Impacts on nature and natural resources, and the related adaptation measures . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 163 6.2.4 Impacts on industries, infrastructure and human well-being, and the related adaptation measures . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 177 6.2.5 I ...
Abrupt rise in atmospheric CO2 at the onset of the Bølling/Allerød: in
... the temporal development of its prognostic variables over time as functions of changing boundary conditions, representing the climate forcing. These prognostic variables are (a) carbon (as dissolved inorganic carbon DIC in the ocean), (b) the carbon isotopes δ 13 C, 114 C, and (c) additionally in th ...
... the temporal development of its prognostic variables over time as functions of changing boundary conditions, representing the climate forcing. These prognostic variables are (a) carbon (as dissolved inorganic carbon DIC in the ocean), (b) the carbon isotopes δ 13 C, 114 C, and (c) additionally in th ...
Survey of Climate Change Considerations in Federal Environmental
... some provided an aggregate estimate of total emissions, and others merely noted that GHG emissions may occur as a result of the project (without quantifying these emissions or identifying specific sources). This variation was partially due to differences in the nature and location of the proposed ac ...
... some provided an aggregate estimate of total emissions, and others merely noted that GHG emissions may occur as a result of the project (without quantifying these emissions or identifying specific sources). This variation was partially due to differences in the nature and location of the proposed ac ...
Geoengineering: Governance and Technology Policy
... (CDR) method or a solar radiation management (SRM) method. CDR methods address the warming effects of greenhouse gases by removing carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere. CDR methods include ocean fertilization, and carbon capture and sequestration. SRM methods address climate change by increasing ...
... (CDR) method or a solar radiation management (SRM) method. CDR methods address the warming effects of greenhouse gases by removing carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere. CDR methods include ocean fertilization, and carbon capture and sequestration. SRM methods address climate change by increasing ...
Carbon cycle modelling and the residence time of natural
... wet chemical techniques. Critique has also been directed to the analytical methodology and sampling error problems (Jaworowski et al., 1992 a; and Segalstad, 1996, for further references), and the fact that the results of the measurements were "edited" (Bacastow et al., 1985); large portions of raw ...
... wet chemical techniques. Critique has also been directed to the analytical methodology and sampling error problems (Jaworowski et al., 1992 a; and Segalstad, 1996, for further references), and the fact that the results of the measurements were "edited" (Bacastow et al., 1985); large portions of raw ...
Investment and growth in the time of climate change
... issues. More specifically, in addition to reviewing adaptation priorities for Europe, chapter 2, Mitigate, adapt, or endure: a question of balance, illustrates key factors that determine the optimal balance between climate-change mitigation and adaptation. The findings following from this illustratio ...
... issues. More specifically, in addition to reviewing adaptation priorities for Europe, chapter 2, Mitigate, adapt, or endure: a question of balance, illustrates key factors that determine the optimal balance between climate-change mitigation and adaptation. The findings following from this illustratio ...
Investment and growth in the time of climate change
... issues. More specifically, in addition to reviewing adaptation priorities for Europe, chapter 2, Mitigate, adapt, or endure: a question of balance, illustrates key factors that determine the optimal balance between climate-change mitigation and adaptation. The findings following from this illustratio ...
... issues. More specifically, in addition to reviewing adaptation priorities for Europe, chapter 2, Mitigate, adapt, or endure: a question of balance, illustrates key factors that determine the optimal balance between climate-change mitigation and adaptation. The findings following from this illustratio ...