* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Genetics
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of diabetes Type 2 wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Saethre–Chotzen syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Gene desert wikipedia , lookup
The Selfish Gene wikipedia , lookup
Human leukocyte antigen wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Gene nomenclature wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
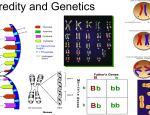
Genetics The study of heredity Vocabulary • • • • Heredity—the passing of traits from parent to offspring. Traits—a trait is a characteristic; hair color, height, ear lobes… Probability—the mathematical chance that an event will occur. Polygenic Inheritance: when more than one gene controls the trait. When this happens you get a variety of sizes or colors. • Types of traits DOMINANT • Dominant traits—the trait observed when at least one dominant allele for a trait is inherited. • Examples: brown eyes, curly hair, dimples, freckles. • TYPES OF TRAITS RECESSIVE Recessive traits are traits that show up only when two recessive alleles for the same trait are inherited. Examples are green eyes, red hair and nearsightedness. Comparing Genes and alleles gene Alleles • • Segments of DNA found on chromosomes Alleles are different forms of a single gene Genotype and phenotype • Genotype -- the inherited combination of alleles. • • • AA Aa aa • Phenotype – the physical appearance of an individual. Homozygous (purebred) heterozygous (hybrid) ALLELE COMBINATIONS Homozygous • Homozygous is when there are two identical alleles of a particular gene present. homozygous • Homozygous is when there are two identical alleles of a particular gene present. • If the letter T represents height, then a capital T = tall and t = short. • A homozygous trait would be either • TT (homozygous tall) • or tt (homozygous short). • PUREBRED is another word for homozygous. It is the result of all dominant or all recessive genes. heterozygous • A heterozygous trait is when two different alleles of a particular gene show up. heterozygous • A heterozygous trait is when two different alleles of a particular gene show up. • If T = tall and t = short, then a heterozygous trait could only be • Tt = (heterozygous tall) • Whenever a capital letter shows up, that trait is DOMINANT, and the recessive trait will not show up in the individual. • HYBRID is another word for heterozygous. It is the result of a dominant gene and a recessive gene. Incomplete dominance • Incomplete dominance refers to a situation where one allele does not completely dominate another allele, and it results in a new phenotype. There is a blending of color. • Examples: • 1. A red snapdragon flower breeds with a white snapdragon flower and their offspring will be a pink snapdragon. (RR red + WW white= RW pink) 2. Two mousies breed, one black and one white and their offspring is a gray mouse. (BB black + W W white = BW gray) CoDominance • Codominance is when both alleles for a gene are expressed and both alleles show up in some form. codominance • Codominance is when both alleles for a gene are expressed and both alleles show up in some form. • Examples: 1. When cattle with red hair and cattle of white hair breed, the resulting offspring will have a coat color of roan, a combination of the red hair and the white hair. 2. In a certain fish, blue scales and red scales are codominant. When a fish has the genotype BR, it has a patchwork of blue and red scales. Multiple gene (allele) inheritance • Multiple gene inheritance is when more than one gene controls the trait. When this happens you get a variety of sizes or colors. It is also known as ‘polygenic’ inheritance. • Examples 1. More than one gene controls eye color, so humans have a variety of eye colors from bright blue to hazel and green to dark brown, almost black. 2. Skin color, height and hand spans are also polygenic. • Betty and Barney Rubble Pedigree—the recorded ancestry of an organism Hemophilia and queen victoria’s family Period 1 Period 3 Period 4 Period 5 Period 6 Period 7 All classes 157 students 50:50 LAB 50:50 LAB COMPARING GRAPHS 50:50 LAB HAND SPAN LAB Hand span and 50:50 lab follow up questions Write down the sentence starter and fill in the blank. 1. There were differences in the curves because _________________________________________. 2. The sample size was ___________________ in the _________________________lab. 3. The Hand span lab was an example of ________________inheritance 4. The 50:50 lab simulated the p__________________ of families having boys or girls. Punnett Square: a model used to show the possible ways genes can combine during fertilization. T= tall t = short (representing alleles) Capital letters are dominant, lower case are recessive. Two alleles from each parent are passed on to offspring T T TT t T t Heredity Sentence Frame Review 1. ___________________________ is the same as hybrid. 2. TT is an example of a(n) _________________________ genotype. 3. A(n) _______________ is a different form of a single gene. 4. An example of a ______________________ is hair color. 5. The genetic combination of alleles is called a _____________________. 6. Recessive traits are represented by ____________________ letters. 7. The _______________________ trait is the one that always shows through. 8. Homozygous is also know as ______________________. 9. In a Punnett square, the alleles of the ___________________ are on the outside of the square. 10. The four squares of the Punnett Square represent the probable _______________ of the parents.