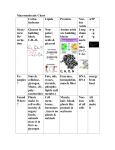
* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Which DNA sequence is most likely to form a hairpin structure? x
Polyadenylation wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Lipid signaling wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Transcriptional regulation wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
G protein–coupled receptor wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
RNA silencing wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
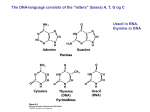
Which DNA sequence is most likely to form a hairpin structure? x indicates any nucleotide. A. xxxGTCAGTxxxxTATGCGxxx B. xxxTCGTATxxxxGTCCGAxxx C. xxxCACTGTxxxxGTACTGxxx D. xxxGTCAGTxxxxCCTAGAxxx E. xxxGTCATCxxxxGATGACxxx RNA is ribonucleic acid and DNA is deoxyribonucleic acid. The difference in the structure of DNA as opposed to RNA is the lack of a hydroxyl group at what position of the ribose? A. 1’. B. 2’. C. 3’. D. 4’. E. 5’. Which statement about RNA is NOT true? A. RNA can base pair with another RNA molecule. B. RNA can base pair with a DNA molecule. C. RNA is commonly found in a double helix structure. D. RNA molecules can form a wide variety of three-dimensional structures. E. RNA contains the nucleotides adenylate, guanylate, cytidylate, and uridylate. Complete the following sentence. Nucleic acids A. can be double-stranded or single-stranded. B. contain equal percentages of all four common nucleotide bases. C. contain covalently linked lipid molecules. D. are formed by a series of nucleotide bases connected by peptide bonds Which of the following statements about B-DNA is FALSE? A. The amount of A+G is equal to the amount of T+C. B. Each of the two strands has the same nucleotide sequence. C. The 5’-end of one strand is paired with the 3’-end of the other strand. D. Base stacking interactions contribute to the stability of the three-dimensional structure. Which of the following molecules carries genetic information that is translated to form protein molecules? A. ribosomal RNA (rRNA). B. transfer RNA (tRNA). C. messenger RNA (mRNA). D. ribosomes. The deoxyribonucleotide polymer (5')CGAACTAGTG(3') will form a double-stranded structure with: A. (5')CACTAGTTCG(3') B. (5')CACUAGUUCG(3') C. (5')CACUTTCGCCC(3') D. (5')GCTTGATCAC(3') Which statement about RNA is TRUE? A. RNA contains the nucleotides adenylate, guanylate, thymidylate, and uridylate. B. RNA can not base pair with a DNA molecule. C. RNA is commonly found in a double helix structure. D. RNA molecules are readily hydrolyzed in basic solution. Which of the following is a similarity concerning DNA versus RNA? A. DNA and RNA are each constructed from adenylate, guanylate, cytidylate, and uridylate B. In each deoxyribose units are connected by 3',5'-phosphodiester bonds. C. In DNA and RNA the amount of G always equals the amount of C. D. Both molecules have an overall negative charge at pH 7. Which DNA sequence is most likely to form a hairpin structure? A. (5’)TGTCATCAAAAGATGACA(3’) B. (5’)CTCGTATAAAAGTCCGAA(3’) C. (5’)ACACTGTAAAAGTACTGT(3’) D. (5’)GGTCAGTAAAATATGCGA(3’) Nitrites, nitrates, and nitrosamines generate nitrous acid, resulting in which of the following? A. Break phosphodiester bonds in RNA B. Promote deamination of bases in DNA C. Accelerate depurination of deoxynucleotides D. Cause formation of thymine dimers. Which of the following statements is correct concerning structures A and B to the right? A. B is the parent compound for adenine and guanine B. A is a purine and B is a pyrimidine C. A is more easily deaminated than B D. B is found in RNA and A in DNA. A B Which of the molecules below results from the deamination of guanine? A. 1 B. 2 C. 3 D. 4 1 2 3 4 Rank the following double-stranded DNA molecules in order of lowest melting temperature to highest melting temperature. Write the letter of the double-stranded DNA in the corresponding blank. Explain why you ranked the DNA molecules in the order you did. A. 5’-CATGTGTACTGTCTGTACATTTCAGATCC-3’ 3’-GTACACATGACAGACATGTAAAGTCTAGG-5’ B. 5’-AGCTCGCTACGGCTATCGCTATCGCGTGT-3’ 3’-TCGAGCGATGCCGATAGCGATAGCGCACA-5’ C. 5’-TACTATTGTTTATACTATATCGTTATATC-3’ 3’-ATGATAACAAATATGATATAGCAATATAG-5’ lowest melting temperature _____ _____ _____ highest melting temperature DNA molecules in the aqueous environment of our cells are often a double helix, the most common form termed B-DNA. Describe the details of noncovalent interactions that stabilize the structure of BDNA in our cells. In the laboratory you observed that a double-stranded DNA molecule containing a sequence consisting of all guanines and cytosines requires a much higher temperature to melt (the two strands of DNA will pull apart) than a double-stranded DNA molecule containing a sequence consisting of all thymines and adenines. Explain the chemical and structural basis for this observation. Palmitic acid is denoted by A. 18:2912 B. 18:19 C. 18:0 D. 16:0 Stearic acid is denoted by A. 18:19 B. 18:391215 C. 16:19 D. 18:0 Oleic acid is denoted by A. 18:2912 B. 18:19 C. 14:0 D. 16:0 Linolenic acid is denoted by A. 18:391215 B. 18:19 C. 16:391215 D. 16:2912 Myristic acid is denoted as A. 16:29,12 B. 18:19 C. 14:0 D. 16:0 Linoleic acid is denoted as A. 18:29,12 B. 18:19 C. 18:0 D. 16:19 Which of the following fatty acids has the highest melting temperature? A. palmitate B. stearate C. oleate D. linolenate Which of the following fatty acids has the lowest melting temperature? A. palmitate B. stearate C. oleate D. linolenate Which of the following fatty acids would have the lowest melting point? A. palmitate. B. stearate. C. oleate. D. linoleate. E. myristate. In the laboratory you switch a culture of E. coli from growth at 4ºC to growth at 40ºC. Which of the following fatty acids would become more plentiful in the cell membrane upon increased growth temperature? A. oleate B. palmitate C. linoleate D. arachidonate E. palmitoleate Which of the following statements is TRUE about biological membranes? A. Biological membranes tend to exclude sterols. B. Biological membranes contain a large proportion of free fatty acids. C. Biological membranes tend to exclude glycerophospholipids. D. Biological membranes have properties affected by the presence and number of double bonds in fatty acids. E. Biological membranes are devoid of proteins. What property of the membrane is most affected by the degree of saturation of fatty acids? A. Fluidity. B. Thickness. C. Curvature. D. Lateral diffusion of proteins. E. Water permeability. Which of the following statements about membranes is true? A. All proteins associated with biological membranes span the lipid bilayer at least once. B. Phospholipids can readily undergo lateral diffusion within the bilayer. C. Phospholipids can readily flip-flop from the inner to outer membrane surface. D. All carbohydrate residues attached to proteins in the membrane face the interior of the cell. E. Biological membranes are freely permeable to ions. What lipid group, when covalently attached to a protein, anchors the protein to the extracellular side (outside) of the plasma membrane? A. farnesyl. B. geranylgeranyl. C. glycophosphatidylinositol. D. myristoyl. E. palmitoyl. The type of membrane transport that uses ion gradients as the energy source is: A. secondary passive transport B. passive transport. C. primary active transport. D. secondary active transport. Which amino acids are most likely to be present lining the inside of a membrane-spanning K+ ion channel? A. Phe, Trp, Val B. Arg, Lys, His C. Glu, Ser, Asp D. Cys, Lys, Ser Consider a cell with extracellular calcium (Ca2+) and chloride (Cl-) concentrations of 5 mM and 10 mM while the intracellular concentrations of Ca2+ and Cl- are 0.01 mM and 100 mM. The transmembrane membrane potential is –90 mV, negative inside. Which is true? A. The chemical force due to the concentration gradient would favor flow of Cl - into the cell. B. The electrical force due to the transmembrane gradient would favor flow of Cl - into the cell. C. Both the chemical force and the electrical force would favor flow of Ca 2+ into the cell. D. Cl- is at equilibrium and no net flow of Cl- would occur. E. Ca2+ is at equilibrium and no net flow of Ca2+ would occur. A nerve cell (neuron) has an intracellular potassium concentration ([K+]in) of 250 mM and an extracellular potassium concentration ([K+]out) of 5 mM. Suppose there is a K+ channel present in the membrane of the nerve cell that opens in response to choline, a product of the breakdown of acetylcholine catalyzed by the enzyme acetylcholinesterase. What would happen after a nerve impulse when acetylcholinesterase catalyzes the breakdown of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine? A. The K+ channel would open and K+ would flow into the neuron. B. The K+ channel would close and K+ flow into the neuron would stop. C. The K+ channel would open and K+ would flow out of the neuron D. The K+ channel would open but there would be no K+ flow because K+ is at its equilibrium potential. E. The K+ channel would close because there is no choline to trigger channel opening. Explain the differences between passive transport and active transport across a membrane. You are studying a protein that you know contains one transmembrane-spanning alpha helix. You have just obtained the amino acid sequence for the protein, shown below. Predict what region of the protein is most likely to span the lipid bilayer and underline the amino acids that are most likely to be the membrane-spanning alpha helix. Explain the criteria you used to decide the region that spans the lipid bilayer. +H N-HGADERTPLCNFGGSTGGACLPMGHFALVLAMYLAAWVLLAVWIFTSRDLEACTCHRDEPGTYSDEGHCR-COO3 Which of the following is often involved in the process of signal transduction? A. Interactions between receptor and second messenger molecules B. Transport of signal molecules, for example hormones, across the membrane C. Activation of intracellular protein kinases. D. Increased production of carbohydrates in the nucleus Which of the following statements concerning receptor enzymes is FALSE? A. They are usually membrane-associated proteins. B. They have an active site on the extracellular side of the membrane. C. They contain an enzyme activity that acts on the inside of the cell. D. They have a ligand-binding site on the extracellular side of the membrane. Fill in the blanks. The G subunit of heterotrimeric G proteins is an important activator of the enzyme __________, which produces the second messenger molecule _____________. A. adenylate cyclase (AC) and cyclic AMP (cAMP). B. phospholipase C (PLC) and SH2 (src-homology 2). C. adenylate cyclase and IP3 (inositol triphosphate). D. phospholipase C and cyclic AMP. E. receptor tyrosine kinase and SH2. G proteins function as molecular switches They are turned “on” by G protein-coupled receptors. What turns them “off” (deactivates them following receptor activation)? A. cAMP phosphodiesterase. B. Dissociation of neurotransmitter bound to the G protein-linked receptor. C. phosphorylation of the subunits. D. phosphorylation of the subunits. E. Endogenous GTPase activity of the G subunit which hydrolyzes GTP to GDP. Trimeric G proteins are signaling molecules A. with an alpha subunit that binds to GTP. B. that transform GTP into cyclic GMP. C. that are found in the nucleus. D. associated with the outer face of the plasma membrane. E. that are activated by a serine/threonine kinase. Protein kinase A A. is a tyrosine kinase. B. is an enzyme that phosphorylates other proteins on serine and threonine residues. C. is a multimer made of four identical subunits. D. contains two regulatory subunits that activate the enzyme when they are associated with two catalytic subunits in a tetrameric complex. E. binds to cyclic AMP and transforms it into ATP. Explain, in chemical terms, why butter is solid at room temperature while vegetable oil is a liquid. When a person with type A blood receives a transfusion of type B blood agglutination (clumping of red blood cells) occurs. Explain why this occurs, including the types of molecules involved and the interactions that play a role in this process. Both carbon dioxide (CO2) and bicarbonate (HCO3-) need to enter and exit an erythrocyte (red blood cell). The erythrocyte membrane contains proteins that transport HCO3- but not CO2. Why is this the case? Why is the rate of Na+ ion flow through the acetylcholine receptor (an ion channel) typically so much greater than the rate of Na+ ion transport by the Na+ / K+ ATPase? Membranes contain various types of proteins. Discuss the differences between the types of membrane proteins, highlighting differences in amino acid sequences, structural features and how the membrane interaction occurs. The sodium channel of neurons and the Na+K+ ATPase both mediate the passage of sodium ions across the membrane. Predict the relative rates of sodium passage across the membrane mediated by each of the proteins. Which is faster? Explain why you gave the answer you did. Phospholipases are enzymes important for many membrane-associated processes. Describe the general reaction catalyzed by phospholipase A2 and the role the enzyme plays in the synthesis of eicosanoid hormones.