* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Microfilaments Intermediate Filaments Extracellular Matrix
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Protein phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
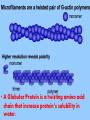
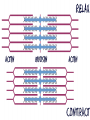
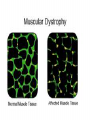
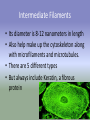
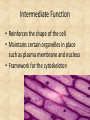
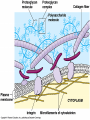
Microfilaments, Intermediate Filaments, AND Extracellular Matrix By David Ryu AP Biology Who discovered Microfilaments? • Paul Wintrebert discovered the cytoskeleton in 1931. • And microfilaments and intermediate filaments are part of the cytoskeleton Microfilaments • • • • Polymers of actin(a globular protein) Each rod is about 7 nanometers long They are present in all eukaryotic cells Exists in edges of cells • A Globular Protein is a twisting amino acid chain that increase protein’s solubility in water. Microfilament Function • • • • Help make up the cytoskeleton Bears tension in muscle contraction Supports cell membrane and structure Thousands of microfilaments exist parallel with each other, “interdigitated” with myosin. Microfilaments Diseases • Muscular Dystrophy -Inherited genetic disorder -Actin can’t connect to plasma membranes • When muscles contract, the actin doesn’t bear tension • Weakens the plasma membrane • Intermediate filaments Cool Fact About Microfilaments •Microfilaments have a fast-growing end and a slow-growing end, and fast-growing end is directed outward! Intermediate Filaments • Its diameter is 8-12 nanometers in length • Also help make up the cytoskeleton along with microfilaments and microtubules. • There are 5 different types • But always include Keratin, a fibrous protein Intermediate Function • Reinforces the shape of the cell • Maintains certain organelles in place such as plasma membrane and nucleus • Framework for the cytoskeleton Facts on Intermediate Filaments! •Even if a cell dies, intermediate filament networks will still live on, maintaining the cell structure! Extracellular Matrix • Cellulose: Plant Cells to Extracellular Matrix: Animal Cells 1. Collagen-most abundant protein and forms strong fibers 2. Fibronectin- protein that glues ECM to Integrin 2. Integrin- surface receptor proteins built into plasma membrane Proteoglycans • These glycoproteins are woven inside a network of proteoglycans, or a proteoglycan complex -Proteoglycan is a protein core with many sugar chains attached covalently -Proteoglycan complex - a long polysaccharide attached by hundreds of proteoglycans attached noncovalently Cool Facts on ECM • The carbohydrate chains attached to the protein cells in proteoglycan keeps your skin healthy and smooth. • The less chains attached, the more wrinkles in your skin will get-aging! Credits • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • http://www.google.com/imgres?q=microfilaments&hl=en&sa=X&biw=1440&bih=702&tbm=isch&p rmd=imvns&tbnid=FI2UNChx19lhttp://www.wisegeek.com/what-are-globular-proteins.htm http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK21560/ http://www.biog1105-1106.org/demos/105/unit1/fibrous_v_glob.html http://www.google.com/imgres?q=microfilaments&num=10&h http://www.biology4kids.com/files/cell_microfilament.html http://www.cytochemistry.net/cell-biology/intermediate_filaments.htm http://www.daviddarling.info/encyclopedia/G/globprot.html http://www.chemistryexplained.com/Ge-Hy/Globular-Protein.html#b http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK21560/ http://www.spainfitness.com/en/beauty-and-bodycare/articulo/proteoglycans.html http://www.enerex.ca/en/articles/amino-sugars http://classes.kumc.edu/som/cellbiology/cytoskeleton/microfilaments/tut8.html http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Muscular_dystrophy http://www.encyclopedia.com/topic/Cytoskeleton.aspx http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15690074 AP Biology book This concludes my presentation • Any Questions? • Thank you for watching!