* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Processes and energy
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
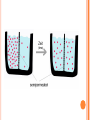
CELL PROCESSES AND ENERGY Cells Unit 2, Part II H. Carter ELEMENTS AND COMPOUNDS Elements Any substance that cannot be broken down into simpler substances Smallest unit= atom Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus, sulfur= found in living things Compounds Two or more elements that are chemically combined Smallest unit= molecule Water two-thirds of your body most chemical rxns w/in cell take place when dissolved water help cells keep size and shape keeps cell from changing temperature too rapidly Inorganic compound Do not contain carbon Water, sodium chloride (table salt) Organic compounds Contain carbon Carbohydrates •Made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen •Sugars and starches •Energy •Found in cell walls, cell membranes Lipids • Made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen •Fats, oils, waxes •Energy-rich (more than carbs) for later use Proteins •Made of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and sometimes sulfur •Meat, fish, eggs, nuts, beans •Made of amino acids •Enzyme- speeds up or slows down a chemical rxn Nucleic Acids •Made of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus •Contain instructions for cell DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid)- genetic material, directs all cell functions; found in chromatin RNA (ribonucleic acid)- role in production of proteins; found in cytoplasm and nucleus CELL TRANSPORT *Cell membrane is selectively permeable which means that certain things can pass w/in the cell while others cannot Diffusion Process by which molecules move from an area of greater concentration to lesser concentration (high to low) Molecules are always moving and collide with each other Collisions cause the molecules to move away from each other to more open space Osmosis Diffusion of water molecules through a selectively permeable membrane Because cells cannot function properly w/out adequate water, many cell processes depend upon osmosis V:\hcarter\Cell Processes\Diffusion_and_Osmosis.asf Normal red blood cell High water concentration Low water concentration outside cell outside cell Passive Movement of materials through the cell membrane that does not require cellular energy V:\hcarter\Cell Processes\Passive transport 4.00.asf Active Transport Movement of materials through the cell membrane using cellular energy Low to high (lesser concentrated to greater) Transport Methods of Active Transport Transport Proteins proteins in the cell that “pick-up” molecules outside cell and carry them in or molecules inside of cell and carry them out Engulfing cell membrane surrounds and encloses a particle *Cells are the small size that they are in order for them to have an easier job in doing their jobs V:\hcarter\Cell Processes\Active transport 5.33.asf PHOTOSYNTHESIS Process by which a plant captures energy from the sun and uses it to make food Nearly all living things obtain energy either directly or indirectly from the sun Stage 1 Capturing the sun’s energy Green pigments in chloroplasts called chlorophyll absorb sunlight In plants, mostly occurs in the leaves Stage 2 Using energy to make food Cell uses the captured energy to make sugars Needs water and carbon dioxide to do this (reactants) Produces a sugar and oxygen (products) light energy 6 CO2 + 6 H2O Carbon dioxide water C6H12O6 + 6 O2 a sugar V:\hcarter\Cell Processes\Photosynthesis.asf oxygen CELLULAR RESPIRATION Process by which cells obtain energy from glucose Cells break down simple food molecules such as sugar and release the energy they contain When cells need energy, they “withdraw” it by breaking down the carbs in the process of respiration Stage 1 Takes place in the cytoplasm Molecules of glucose are broken down into smaller molecules Oxygen is not involved Small amount of energy released Stage 2 Takes place in the mitochondria Small molecules are broken down into even smaller molecules Requires oxygen and releases a large amount of energy Uses sugar and oxygen (reactants) Releases carbon dioxide, water, and energy (products) C6H12O6 + 6 O2 sugar oxygen 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + energy carbon dioxide water V:\hcarter\Cell Processes\Cellular_Respiration.asf COMPARING PHOTOSYNTHESIS AND CELLULAR RESPIRATION They are OPPOSITES! FERMENTATION An energy releasing process that does not require oxygen Provides energy for cells Energy release is much lower than for cellular respiration Alcoholic Fermentation: occurs when yeast and other unicellular organisms break down sugars Bakers, brewers Lactic Acid Fermentation: occurs in muscles when your muscle cells use up oxygen faster than it can be replaced Product is lactic acid; causes pain, soreness