* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Junctions II
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Gap junction wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
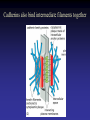
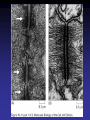
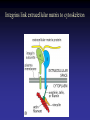
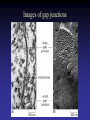
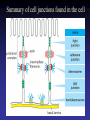
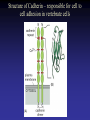
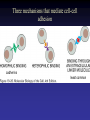
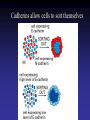
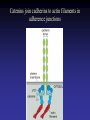
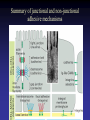
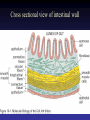
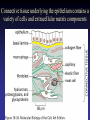
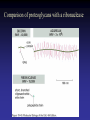
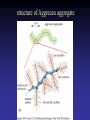
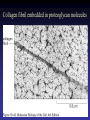
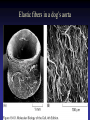
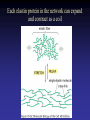
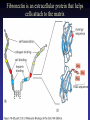
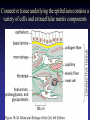
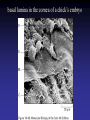
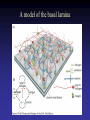
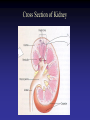
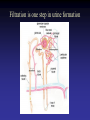
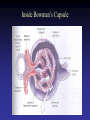
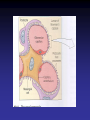
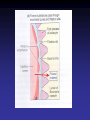
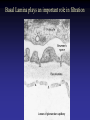
Cell Junctions and extra cellular matrix II chapter 19 Desmosomes and hemidesmosomes both link to intermediate filaments Cadherins also bind intermediate filaments together Integrins link extracellular matrix to cytoskeleton Size of gap junction channel can be determined with fluorescent molecules of different sizes A Gap junction connexon is made up of 6 transmembrane connexin subunits Images of gap junctions The permeability of gap junctions can be regulated dopamine treatment reduces permeability of gap junctions to a fluorescent dye Summary of cell junctions found in the cell Summary of cell junctions found in the cell In plant cells plasmodesmata perform many of the same functions as gap junctions View of plasmodesmata Structure of Cadherin – responsible for cell to cell adhesion in vertebrate cells Ca2+ is required to establish cell to cell connection through cadherin Three mechanisms that mediate cell-cell adhesion cadherins least common Cadherins allow cells to sort themselves Catenins join cadherins to actin filaments in adherence junctions Summary of junctional and non-junctional adhesive mechanisms Cells surrounded by extracellular matrix Cross sectional view of intestinal wall Connective tissue underlying the epithelium contains a variety of cells and extracellular matrix components Fibroblasts surrounded by collagen fibrils Glycosaminoglycan (GAG) chains occupy large amounts of space and form hydrated gels Hyaluronan, a simple GAG, occupies a large amount of space, thereby providing mechanical support Repeating disaccharide unit of hyaluronan GAG and its core protein form proteoglycan Comparison of proteoglycans with a ribonuclease picture of aggrecan aggregate, a large proteoglycan structure of Aggrecan aggregate Collagen fibril embedded in proteoglycan molecules Fibroblast surrounded by collagen fibrils Collagen fibrils in tadpole skin This arrangement is also found in bone and the cornea Elastic fibers in a dog’s aorta Each elastin protein in the network can expand and contract as a coil Fibronectin is an extracellular protein that helps cells attach to the matrix Connective tissue underlying the epithelium contains a variety of cells and extracellular matrix components basal lamina in the cornea of a chick’s embryo A model of the basal lamina Cross Section of Kidney Filtration is one step in urine formation Structure of Nephrons Inside Bowman’s Capsule Basal Lamina plays an important role in filtration