* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cytoplasm!
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
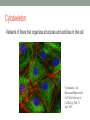
Cytoplasm & Cytoskeleton Cytoplasm! • Cytoplasm is a semi-fluid substance that fills the inside of a cell and surrounds all of the internal structures. • It is present in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells Structure • Gel-like material made of water, proteins, carbohydrates, salts, sugars, amino acids and nucleotides. • Three main constituents: cytosol, organelles, cytoplasmic inclusions • Made of 70-90% water and is usually colorless • Surrounds all internal structures (organelles, nuclear envelope, etc.) • Outer clear glassy layer is ectoplasm, inner layer is endoplasm. • Cytoplasm + nucleus = protoplasm of a eukaryotic cell. • In prokaryotic cells it is basically everything enclosed by the cell membrane (no nucleus). Functions • Most of the cellular activities occur in the cytoplasm. • Where the functions for cell expansion, growth, metabolism, and replication are carried out (in both eukaryotic & prokaryotic cells) • Provides a medium for organelles to remain suspended • Promotes cell efficiency and movement through cytoplasmic streaming • Transports genetic material and products of cellular respiration • Protects genetic material and organelles from damage caused by collisions with other cells Cytoskeleton • Network of fibers that organizes structures and activities in the cell "Cytoskeleton – the Movers and Shapers in the Cell." British Society for Cell Biology. Web. 15 Sept. 2015. Main Functions • Support • Mechanical support • Maintains shape • Aids organelles and cytosolic enzyme molecules • Stabilized by a balance between opposing forces exerted by the elements • Movement • Cell Motility • Change in cell location and movement of cell parts • Cytoskeleton and motor proteins work together Type of Fibers • Microtubules • The thickest • Hollow tubes • Protein Subunits: tubulin • Microfilaments • Thinner • 2 interwined strands of actin • Protein Subunits: Actin • Intermediate Filaments • Fiborous proteins coiled into cables • Protein Subunits: 1 of many different protein (keratin)