* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download presentation source
Radical (chemistry) wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrion wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
15-Hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid wikipedia , lookup
Specialized pro-resolving mediators wikipedia , lookup
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (H+-translocating) wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
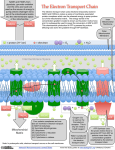
How energy is derived from food. AGRI 6203 Cellular Respiration • Process of oxidizing food – energy released • captured in ATP • Two phases – glycolysis • breakdown of glucose to pyruvic acid – oxidation of pyruvic acid Glycolysis • in eukaryotes, it occurs in the cytosol. • C6H12O6 + 2NAD+ -> 2C3H4O3 + 2NADH + 2H+ • The free energy stored in 2 molecules of pyruvic acid is somewhat less than that in the original glucose molecule. • Some of this difference is captured in 2 molecules of ATP. Glycolysis Fates of Pyruvic Acid in Yeast • Pyruvic acid is decarboxylated and reduced by NADH to form a molecule of carbon dioxide and one of ethanol. • C3H4O3 + NADH + H+ -> CO2 + C2H5OH + NAD+ • This accounts for the bubbles and alcohol in, for examples, beer and champagne. • The process is called alcoholic fermentation. • The process is energetically wasteful because so much of the free energy of glucose (some 95%) remains in the alcohol (a good fuel!). Fate of pyruvic acid in muscles • Pyruvic acid is reduced by NADH forming a molecule of lactic acid. • C3H4O3 + NADH + H+ -> C3H6O3 + NAD+ • The process is called lactic acid fermentation. • The process is energetically wasteful because so much free energy remains in the lactic acid molecule. (It can also be debilitating because of the drop in pH of overworked muscles.) Fate of pyruvic acid in mitochondria • Pyruvic acid is oxidized completely to form carbon dioxide and water. • The process is called cellular respiration. • Approximately 40% of the energy in the original glucose molecule is trapped in molecules of ATP. Mitochondrion Mitochondrion • Outer membrane – integral membrane proteins • form channels • Inner membrane - 5 complexes – – – – – NADH dehydrogenase succinate dehydrogenase cytochrome c reductase cytochrome c oxidase ATP synthase Citric Acid Cycle • Each of the 3 carbons present in pyruvate that entered the mitochondrion leaves as a molecule of CO2 • at 4 steps in the cycle, a pair of (2e-) is removed and transferred to NAD+ reducing to NADH + H+ • at one step, a pair of electrons is removed from succinic acid and reduces FAD to FADH2 • one GTP (ATP equivalent is produced) The Respiratory Chain- Function of the four integral membrane proteins • NADH (FADH2) - stepwise transfer of electrons to ________ atoms to form _______. • Harness the energy released by e- transfer to the pumping of protons (H+) from the matrix to intermembrane space • Protons are pumped a 3 complexes – NADH dehydrogenase complex – cytochrome c reductase complex – cytochrome c oxidase complex • an average of three protons are pumped out at each complex as each pair of electrons passes through it – 9 protons are pumped for each pair of electrons from NADH; 6 from each pair from FADH2 • The gradient of protons formed across the inner membrane by this process forms a miniature battery • protons can flow back down this gradient, reentering the matrix, only through ATP synthase, another complex of integral protiens in the inner membrane Chemiosmosis in mitochondria • Energy from electrons is harnessed by – NADH dehydrogenase complex – cytochrome c reductase complex – cytochrome c oxidase complex • the complexes pump protons against their gradient from the matrix into the inner membrane space • a strong diffusion gradient is set up, the only exit of these protons is through ATP synthase complex Sources Kimball’s Biology Pages The Biology Project Principles of Biochemisrty, Lehniger, 1982