* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cellular Respiration
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Radical (chemistry) wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrion wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
15-Hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Specialized pro-resolving mediators wikipedia , lookup
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (H+-translocating) wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
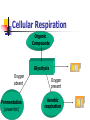
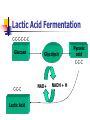
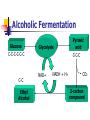
Cellular Respiration Process that involves oxygen and breaks down food molecules to release energy. Anaerobic respiration- without O2. Aerobic respiration- with O2. C6H12O6 + 6O2 6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy (ATP) Cellular Respiration Three parts: 1> Glycolysis: a series of chemical reactions that produces 2 molecules of ATP and 2 molecules of pyruvic acid. 2> Kreb’s cycle: a series of chemical reactions using pyruvic acid to produce ATP and two types of reduced molecules. 3>Electron Transport Chain: the process of extracting ATP from NADH and FADH2 Cellular Respiration Organic Compounds Glycolysis Oxygen absent Fermentation (anaerobic) Oxygen present Aerobic respiration Glycolysis (cytoplasm) Decomposition of glucose to pyruvate Nine intermediate products are formed Each rxn is catalyzed by an enzyme Summarized steps: 1) 2 ATP are added 2) 2 NADH are produced 3) 4 ATP are produced 4) 2 pyruvate are formed Krebs Cycle (mitochondria) Other names: Citric acid cycle or tricarboxylic acid cycle Summarized steps Pyruvate to acetyl-CoA Produced: 1 NADH and 1 CO2 Krebs Cycle Produced: 3 NADH, 1 FADH2, 1 ATP, 2 CO2 Oxidative Phosphorylation Electron Transport Chain (ETC) Inner membrane of the mitochondria Electrons from NADH and FADH2 are passed along the ETC Electrons are passed from one carrier protein to another along the chain, losing energy at each step. Cytochromes and various other proteins participate as carrier proteins in the chain Cytochrome c Final electron acceptor is Oxygen Fermentation Two common types Lactic Acid Fermentation Production of lactic acid from pyruvic acid Alcohol Fermentation Production of ethyl alcohol from pyruvic acid >No ATP production. >Regenerate NAD+, keeps glycolysis going to make more ATP. Lactic Acid Fermentation C-C-C-C-C-C Glucose Glycolysis Pyruvic acid C-C-C C-C-C Lactic Acid NAD+ NADH + H Alcoholic Fermentation Glucose Glycolysis C-C-C-C-C-C C-C Ethyl Alcohol Pyruvic acid C-C-C NAD+ NADH + H+ CO2 2-carbon compound