* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Translation text
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Polyadenylation wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
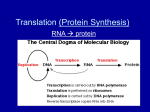
Translation In order to understand the message we must first know what the message in mRNA means. - Bases that code for amino acid are called a codon (triplets eg. AUG) - there are only 20 amino acids and about 64 possible codons - first two nucleotides are consistent for a particular amino acid, but the third nucleotide can vary and still code for the same amino acid - this third amino acid is called the wobble position - this allows for more than one codon to code for an amino acid in the case of error mRNA - Once the mRNA is modified, it leaves the nucleus through a nuclear pore and enters the cytoplasm - in the cytoplasm, it moves to the rough endoplasmic reticulum (which is covered by ribosomes) or to free ribosomes to make protein - once the mRNA is in the cytoplasm, the ribosome works with the tRNA to make protein Transfer RNA (tRNA) - capable of attaching to an amino acid at top near the acceptor stem; at bottom has anticodon loop that is the compliment of the codon found on mRNA - like mRNA transcribed but does not stay linear - folds into three lobed shape - at end of one lobe is anticodon; complimentary to codon of mRNA molecule - at 3’ end is attachment site for amino acid; particular aa specified by mRNA codon - tRNA molecule bound to aa = amino-acyl tRNA (aa-tRNA) Activating enzyme - responsible to attach correct aa to tRNA molecule - 2 binding sites: 1 recognizes aa, other recognizes anticodon on tRNA molecule - enzyme catalyzes reaction that attaches aa to 3’ hydroxyl group - aa-tRNAbinds to specific codon on mRNA that matches anticodon Ribosomes - brings mRNA, aa-tRNA, and enzymes that build polypeptides together - complex of proteins with rRNA (ribosomal RNA) - rRNA form 2 subunits; large and small sub-units - rRNA is linear strand of RNA that is always bound to proteins in ribosome assembly - rRNA sandwiched between units - rRNA strands in ribosome provide binding site for mRNA and 3 binding sites for tRNA - P-site : holds one aa-tRNA with growing aa chain - A site : holds tRNA bringing next aa to add to chain - E site : exit site Initiation - sequence of nucleotides at 5’ end of mRNA (leader sequence) binds to rRNA in small ribosomal sub-unit - initiator tRNA binds to ribosomal-mRNA complex; has anticodon UAC - this is complement to start codon AUG which carries methionine (aa) and starts translation - first aa-tRNA carrying methionine begins the process by sitting on the P Site Elongation - mRNA codon exposed in A binding site forms base pair with incoming aa-tRNA - enzymes in large sub-unit catalyze peptide bond between last aa in growing chain and new aa - polypeptide chain transferred from tRNA in P site to tRNA in a site - ribosome moves 3 nucleotides (codon) along mRNA; translocation - this brings pp chain into P site and exposes new A site - tRNA that was in P site now in E site and detaches from ribosome Termination - ribosome will eventually reach the stop codon in A binding site which has no corresponding amino acid - tRNA carrying pp chain stays on P site until protein called a release factor binds to A site recognize that the ribosome has stopped and release the polypeptide chain - the ribosome will break down into subunits and translation stops - the protein folds into its 3-D structure and may be modified with carbohydrates or phosphates and cleaved - it may move to part of the cell where it is needed or packaged to leave the cell through endocytosis --- overall: as soon as first ribosome moved off initiation sequence of mRNA new ribosome assembly can bind to same molecule - this way many ribosomes can attach to 1 mRNA molecule = polyribosome http://highered.mcgraw-hill.com/olc/dl/120077/micro06.swf