* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 6: Alkynes, reactions of alkynes, and multistep synthesis
Elias James Corey wikipedia , lookup
Aromaticity wikipedia , lookup
Cracking (chemistry) wikipedia , lookup
George S. Hammond wikipedia , lookup
Enantioselective synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Homoaromaticity wikipedia , lookup
Wolff–Kishner reduction wikipedia , lookup
Baylis–Hillman reaction wikipedia , lookup
Petasis reaction wikipedia , lookup
Discodermolide wikipedia , lookup
Aromatization wikipedia , lookup
Hydrogenation wikipedia , lookup
Diels–Alder reaction wikipedia , lookup
1,3-Dipolar cycloaddition wikipedia , lookup
Wolff rearrangement wikipedia , lookup
Ene reaction wikipedia , lookup
Stille reaction wikipedia , lookup
Hydroformylation wikipedia , lookup
Ring-closing metathesis wikipedia , lookup
Strychnine total synthesis wikipedia , lookup
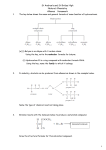
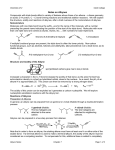
Chemistry 242 Chapter 6: Reactions of Alkynes & Intro to Multi-Step Synthesis Homework: 25a-e, 26, 27, 28, 29, 32, 33, 36, 38, 40, 42, 43, 44, 45, 49, 50 (Solution Manual error: 27e should be 1,5-cyclooctadiene) Outline I. Alkynes A. internal alkyne vs terminal alkyne II. Nomenclature A. common 1. triple bond is acetylene 2. everything else is substituent 3. ex. isopropylmethyl acetylene or t-butylcyclopentylacetylene 4. HCCCH2- is propargyl group, similar to allyl grp (H2C=CHCH2-) 5. ex propargyl alcohol B. IUPAC 1. name like alkenes, but no cis/trans or E/Z 2. find longest chain containing funct. grp and # so funct grp # smallest 3. if 2 triple bonds, diyne a. if 3 trple bonds, triyne b. if 4, tetrayne, then pentayne, hexayne, heptayne, etc 4. with number (#) as prefix a. funct grp has priority with numbering 5. if more than 1 subst., place all in alphabetical order in front 6. if counting from either end is tie in yne #, use subst # for tie-breaker (look for 1st point of difference) 7. if still tied, go to second subst, etc (1st point of difference) 8. #1 in cyclics, other C in pi bond is #2 a. no need to include number of pi bond in name unless diene, when both numbers included b. go clockwise (cw) or ccw to get lowest subst # c. 1st point of difference, not sum of all subst # examples: C. More than one parent nomenclature A. priority table 6.1 (p262) examples: 1 III. Physical properties A. mp, bp, water solubility B. sp hybridized → linear (no cis/trans or E/Z) IV. Reactions of Alkynes A. Electrophillic addition 1. has pi electrons and is a nucleophile just like alkene 2. but can react twice because twice the # pi bonds a. excess reactant 3. alkene more reactive than alkyne a. because of carbocation intermediate stability B. Specific addition rxns 1. hydrogen halides → geminal dihalide 2. straight halogen (bromine or chlorine in CH2Cl2) 3. H2O/H2SO4 → enol a. keto-enol tautomerization (acid cat. or base cat.) b. water sulfuric acid works for internal alkynes c. need mercuric sulfate for terminal alkynes d. can get aldehyde if acetylene 4. Hydroboration-oxidation (1. BH3/THF, 2. HO-, H2O2, H2O) a. antimarkovnikov product b. for terminal alkynes, use isoamyl borane c. easly get aldehyde 5. Hydrogenation a. usually can’t stop at alkene b. can stop only if using “poison” catalyst (Lindlar catalyst) c. get cis alkene for syn addition with Lindlar d. to get trans, use Na or Li in liquid ammonia (-78ºC) e. this is radical addition 2 V. Acidity of terminal alkyne A. very strong base (sodium amide) will pull of proton, creating a nucleophile 1. substitutes onto alkyl halide 2. only reaction so far which enlarges the carbon chain (or changes the length at all) VI. Multistep synthesis A. Most syntheses take more than one step to get from starting molecule to end point. Objectives Knowledge Recall rules for alkyne nomenclature Memorize chapter reactions on p282-283 Comprehension Add vinylic cation to stability list (where and why?) Understand what a polymer is (moved to Chapter 11) Application Name given alkynes or sketch alkyne molecule if given the name Draw mechanisms for bridged bromination/chorination and hydrohalogenation (Chapt 5) Draw mechanism for keto-enol tautomerization Analysis Write a sequence of reactions to get from a given reactant to a desired product Use reaction summary (p282-283) to complete missing part of rxns (react, prod, rxn cond) 3