* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Fig. 6.7a
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
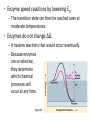
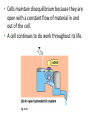
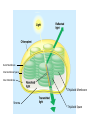
Biological Energetics: Metabolism Enzymes Fig. 6.15 • Enzyme speed reactions by lowering EA. – The transition state can then be reached even at moderate temperatures. • Enzymes do not change ΔG. – It hastens reactions that would occur eventually. – Because enzymes are so selective, they determine which chemical processes will occur at any time. Fig. 6.13 • Reactions in closed systems eventually reach equilibrium and can do no work. • A cell that has reached metabolic equilibrium has a ΔG = 0 and is dead! • Metabolic disequilibrium is one of the defining features of life. Fig. 6.7a • Cells maintain disequilibrium because they are open with a constant flow of material in and out of the cell. • A cell continues to do work throughout its life. Fig. 6.7b • A catabolic process in a cell releases free energy in a series of reactions, not in a single step. • Some reversible reactions of respiration are constantly “pulled” in one direction as the product of one reaction does not accumulate, but becomes the reactant in the next step. Fig. 6.7c Outer Membrane Intermembrane Space Inner Membrane Thylakoid Membrane Stroma Thylakoid Space