* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 2.-B-and-T-lymphocytes
Anti-nuclear antibody wikipedia , lookup
Duffy antigen system wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Lymphopoiesis wikipedia , lookup
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Innate immune system wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Monoclonal antibody wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
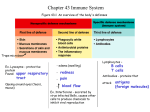
Unit 4 Immunology and Public Health Unit 4 – Immunology and Public Health 1. The Immune System a)Non-specific defences b)Specific cellular defences 2. Infectious Diseases and immunity a)Transmission and control b)Active Immunisation and Vaccination and the evasion of immune responses 1. The Immune System b) specific cellular defences By the end of this section you will be able to ….. • describe the roles of 2 types of Tlymphocytes in response to infection • describe the role of B-lymphocytes in response to infection Lymphocytes • Lymphocytes respond specifically to: – Antigens on foreign cells – Cells infected by pathogens – Toxins released by pathogens Read the Lymphocyte information cards (word doc. Link in unit 4 table on school website) and be able to answer the following questions… B-Lymphocytes T-Lymphocytes • Explain the link between B-lymphocytes and antibodies • What is special about these antibodies? • Describe the 2 effects of an antigen-antibody complex • Explain the role of a ‘memory B cell’ • How many groups of Tlymphocytes are there? • What are the names of the 2 groups? • Explain the link between lymphocytes and apoptosis • Explain the link between lymphocytes and cytokines • Explain how phagocytes and B-lymphocytes are involved B-lymphocytes B lymphocytes are able to recognise foreign antigens and engulf them. They then display the antigens on their surface waiting for a TH cell to release cytokines and activate it. Some will become clone antibody-producing B cells, others become cloned memory B cells Activated B lymphocytes Activated lymphocytes can produce a protein specific to the antigen called antibodies. The antibodies are able to bind to the antigen creating an antigen-antibody complex. Antibody action The binding of the antibodies causes the • inactivation of the pathogen (or the toxin it produces) and • pathogen to become more susceptible to phagocytosis B-Lymphocytes extra note Antibody receptor site Antigen A specific antibody is made by Blymphocytes. Antibodies are secreted into the lymph and blood where they make their way to the infected area. The antibodies recognise a specific surface antigen . Antibody Production • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lrYlZ Jiuf18 • http://www.kscience.co.uk/animations/l ymphocyte.htm Your teaching should allow you and the other pupil to be able to answer these questions… B-Lymphocytes • Explain the link between B-lymphocytes and antibodies • What is special about these antibodies? • Describe the 2 effects of an antigen-antibody complex • Explain the role of a ‘memory B cell’ T-Lymphocytes 1. How many groups of Tlymphocytes are there? 2. What are the names of the 2 groups? 3. Explain the link between lymphocytes and apoptosis 4. Explain the link between lymphocytes and cytokines 5. Explain how phagocytes and B-lymphocytes are involved T-lymphocytes 1. There are two different types of T-lymphocytes or T-cells. 2. - cytotoxic T cells (TC cells) AKA Killer T cells - helper T cells (TH cells) 3. Cytotoxic T cells cause apoptosis of an infected cell (programmed cell death) • remember NK cells! TC cells and cancer TC cells are also able to recognise antigens found on the surface of cancer cells. They are then able to bring about the lysis of large cancer cells. T-lymphocytes 4. Helper T cells become activated when they have come into contact with a foreign antigen and produce cytokines. 5. The cytokines then activate other cells (B-lymphocytes and phagocytes) TH Cells As seen before, there is a vast pool of different TH cells with different forms of antigen receptors. One of them will be specific to the antigen. Helper T-lymphocytes (TH Cells) ANOTHER way helper T cells can remove pathogens, is when phagocytes engulf the foreign cell This phagocyte then presents the foreign antigen on its own surface, meaning one of the TH cells will be able to bind with it. Antigen presenting cell Helper T-Lymphocytes extra notes • When pathogens infect a tissue, some phagocytes capture the pathogen and display the it’s antigens on their surface • This display of antigen presentation, activates T-lymphocytes. • Once one version of the TH cell is activated, it goes on to multiply to give further clones of activated TH cells Key Area 2 Key words (so far!) Create a WORD BANK/ GLOSSARY • Cytokine • Clonal selection theory • B-lymphocyte • Cytotoxic T cell • Helper T cell • Antibody • • • • • Antigen Phagocytosis Phagocyte Apoptosis Cell lysis Can you now …. • Describe the roles of 2 types of Tlymphocytes in response to infection • Describe the role of B-lymphocytes in response to infection