* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download All organisms are made of cells
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
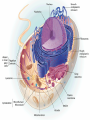
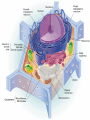
All organisms are made of cells Ch. 6.1 Cells are the basic part of biology ALL organisms are made of cells The Cell Theory Microscopes have made it much easier to begin to understand cells 1st light microscopes were developed around 1600 Robert Hooke was the 1st to look at cork (oak bark) using a light microscope Had compartments; named CELLS CELL THEORY generalization that ALL living things are composed of cells. Microscopes as Windows to Cells Light Microscopes can magnify objects up to about 1,000 times Much of the cell structure is smaller than that! Can use other microscopes Scanning electron microscope Transmission electron microscope An Overview of Animal and Plant Cells Each part of a cell with a specific job to do is an ORGANELLE(mini organ) Previous slides show a diagram of both an animal cell and a plant cell Many differences Many similarities PLASMA MEMBRANE defines the boundary of the cell and regulates traffic btwn cell and its surroundings NUCLEUS holds the genetic material of the cell (DNA) Both have CYTOPLASM holds dif. organelles suspended in fluids Plant cells have a CELL WALL; animal cells don’t. Two Major Classes of Cells PROKARYOTIC lacks a nucleus and most organelles Bacteria EUKARYOTIC has a membraneenclosed nucleus and organelles Plants Fungi animals Concept Check What evidence led to the development of the cell theory? How do the various kinds of microscopes differ as tools in the study of cells? Identify two similarities and two differences between plant and animal cells. How is a eukaryotic cell different from a prokaryotic cell?