* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Topic 1
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
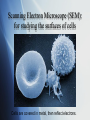
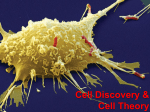
Discovery and study of cells Unit 2 part1 Packet 4 Cell biology pioneers Robert Hooke (1665) Examined cork under a simple microscope…described what he saw as “little rooms” (cellulae, Latin) Anton van Leeuwenhoek (1674) Also used rudimentary microscope to examine many things…blood, pond water, scrapings of plaque from teeth. Described what he saw as animicules…the first descriptions of bacteria and protists. Light Microscopes Magnification vs. Resolution Magnification increase in size Resolution measure of clarity Electron Microscopes Use a beam of electrons instead of light SEM and TEM Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM): for studying the internal structure of cells Spinach Cell Chloroplast Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM): for studying the surfaces of cells Cells are covered in metal, then reflect electrons. SEM A View of the Cell We’ve come a long way since the time of Hooke (1665) thanks to more sophisticated microscopes. By the mid-1800s there was an established cell theory. Cell Theory Cells are the basic unit of organization of living things Every living organism is made of one or more cells All cells come from other cells already in existence Types of cells Two major categories: Prokaryotic Eukaryotic Two subcategories: Plant Animal Organisms made of eukaryotic cells can be unicellular or multicellular