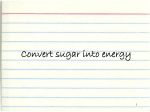* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Eukaryotic Cells
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
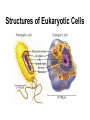
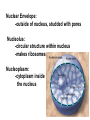
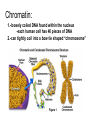
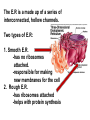
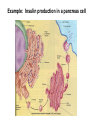
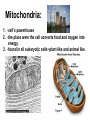
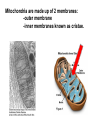
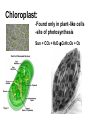
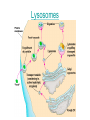
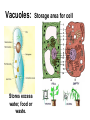
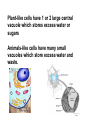
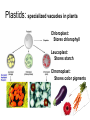
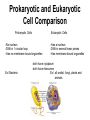
Structures of Eukaryotic Cells Nucleus: 1.-Brain of cell , the cells control center 2.-Surrounded by another membrane/nuclear envelope 2.- Contains DNA -has code for making all proteins/traits of cell 4.- Contains pores for items to move in and out. Nuclear Envelope: -outside of nucleus, studded with pores Nucleolus: -circular structure within nucleus -makes ribosomes Nucleoplasm: -cytoplasm inside the nucleus Chromatin: 1.-loosely coiled DNA found within the nucleus -each human cell has 46 pieces of DNA 2.-can tightly coil into a bow tie shaped “chromosome” Chromosomes are made up of genes. Genes: -segments of DNA which code for specific proteins These proteins determine our traits. Ribosomes: The cells “workbench” Job: Makes proteins, in their linear form, by assembling amino acids in the correct order based on DNA’s code. Ribosomes are made up of RNA and proteins. Found attached to the endoplasmic reticulum or Free floating in the cytoplasm Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER): -Known as the “cells subway system -Transports proteins around the cell The E.R is a made up of a series of interconnected, hollow channels. Two types of E.R: 1. Smooth E.R. -has no ribosomes attached. -responsible for making new membranes for the cell 2. Rough E.R. -has ribosomes attached -helps with protein synthesis 1.Proteins, made by the ribosomes 2.Travel through the hollow channels of the rough ER into the smooth ER. 3. The end of the smooth ER pinches off around the protein forming a “transporting vesicle” 4. Transporting vesicle transports the newly formed protein to the golgi body. Golgi Complex, Apparatus or Bodies -a stack of flattened membranes clustered in one area. -Made up of a collection of transporting vesicles. The golgi is known as the Fed-Ex man Job: Collects, stores, modifies and packages materials it receives from the transporting vesicles/ER and then deliver them to where they need to go. This is where a protein gets it 3D shape Example: Insulin production in a pancreas cell Mitochondria: 1. -cell’s powerhouse 2. -the place were the cell converts food and oxygen into energy. 3. -found in all eukaryotic cells~plant-like and animal like. 4. -site of cellular respiration sugar + oxygen ATP energy + carbon dioxide + water Form of energy used by a cell to do “work”. -12 to 1000 mitochondria per cell -plant cells have less than animal cells. Why? -less active -require less energy -Which cells in our body would have the most mitochondria? -muscle cells ~ very active Mitochondria are made up of 2 membranes: -outer membrane -inner membranes known as cristae. Chloroplast: -Found only in plant-like cells -site of photosynthesis Sun + CO2 + H2OC6H12O6 + O2 CHLOROPLAST: -Trap energy of the sun and convert it into sugars which can be stored by the plant or broken down in the mitochondria into ATP energy. Plant store sugar in their fruits, stems, and roots. ROY G BIV Absorbs: -all spectrums of light but green is reflected. Lysosomes: Nickname: Clean Up Crew or Suicide Sack Job: Organelles which contain digestive enzymes made by the ribosomes and processed in the golgi. Two Jobs: 1. Fuse to an old or damaged cell organelle, injects its enzymes into it and digest the old organelle . 3. Lysosomes in an older or damaged Cell breaks open and releases enzymes into the Cytoplasm ~ digesting the cell from the inside out. Example: lifespan RBC’s WBC’s Sperm 120 days 8 days 5 days Lysosomes See last page of note package: Lysosomes Formation of a lysosome: 1. Ribosomes make a digestive enzyme 2. Enzymes travel through ER 3. Smooth ER pinches off and dig. enzyme is contained in a transporting vesicle. 4. Transporting vesicle fuses with golgi 5. Golgi modifies enzyme giving it a 3D shape 6. Section of golgi moves away with enzyme inside it ~ now a lysosome. Vacuoles: Stores excess water, food or waste. Storage area for cell Plant-like cells have 1 or 2 large central vacuole which stores excess water or sugars Animals-like cells have many small vacuoles which store excess water and waste. Plastids: specialized vacuoles in plants Chloroplast: Stores chlorophyll Leucoplast: Stores starch Chromoplast: Stores color pigments See last page: Centrioles: used by animal cells to help with cell division Plant and Animal Cell Comparison Plant cells have: Animal cells have: cell wall and membrane cell membrane chloroplast no chloroplast 1 or 2 large vacuole many small vacuoles No centrioles 1 pair of centrioles Has plastids No plastids Rectangular in shape Roundish in shape Small # of mitochondria Large # of mitochondria Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cell Comparison Prokaryotic Cells Eukaryotic Cells -No nucleus -DNA in 1 circular loop -Has no membrane bound organelles Ex/ Bacteria -Has a nucleus -DNA in several linear pieces -Has membrane bound organelles -both have cytoplasm -both have ribosomes Ex/ all protist, fungi, plants and animals