* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Genetic Engineering
Zinc finger nuclease wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
DNA profiling wikipedia , lookup
Metagenomics wikipedia , lookup
DNA polymerase wikipedia , lookup
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
Bisulfite sequencing wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
SNP genotyping wikipedia , lookup
DNA damage theory of aging wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom National DNA Database wikipedia , lookup
Genealogical DNA test wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid double helix wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
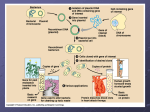
Ch.12 Genetic Engineering Genetic Engineering • Genetic Engineering - It is now possible to directly alter the genetic makeup of an organism. – Cutting DNA – Changing DNA – Removing and reinserting DNA 1 Restriction Endonuclease • Restriction Endonuclease – Recognizes and cuts DNA at a particular sequence. – EcoR1, BamI, HaeIII Restriction Endonuclease 2 Restriction Endonuclease • Sticky Ends – Unpaired DNA bases that result from a cut by a restriction endonuclease. – Can be attached to another molecule of DNA cut with the same restriction endonuclease. Sticky Ends Restriction Endonuclease Sticky Ends 3 Restriction Endonuclease Bacteria • Bacteria – – – – – Prokaryotes - lacks a nucleus Simplest forms of life Very small (nanometers) Reproduce asexually Most abundant and diverse organism in the world. – Some are helpful • Photosynthetic bacteria, bacteria in your large intestine, bacteria on your skin, bacteria that decompose dead organisms…. – Some are harmful • Food poisoning, colds, infections… 4 Bacteria Structure • • • • • • No membrane bound organelles Cell wall - maintains the cell’s shape Capsule - helps the cell attach to surfaces. Flagellum - some bacteria have one or more. Pili - helps the cell stick to surfaces DNA- one molecule of circular DNA Bacteria Structure • Plasmids – Small circular pieces of DNA found in bacteria in addition to their chromosomes. – – – Can be removed from bacteria and cut up using restriction enzymes. A DNA sequence can be inserted into a plasmid. Plasmids can be easily reinserted back into bacteria. 5 Bacteria Structure • Plasmids carry genes for… – – – – – – – resistance to antibiotics resistance to heavy metals sensitivity to mutagens sensitivity or resistance to bacteriophages production of restriction enzymes production of amino acids production of toxins Cloning Genes By Using Bacteria • • Recombinant DNA – Combining DNA from two different sources. Transgenic organism - An organism which contains foreign DNA 6 Cloning Genes By Using Bacteria • Transformation-inserting a plasmid which contains a foreign gene into bacteria – – Remove a plasmid from a bacterium Use a restriction endonuclease to remove a gene from an organism - Create sticky ends! Use the same restriction endonuclease to cut open the plasmidCreate sticky ends! Insert the gene into the plasmid Place the plasmid back into the bacterium – – – Cloning Genes By Using Bacteria • Reasons to do this – – Clone the gene - Many copies of the plasmid are made by the bacteria as the bacteria reproduce Express a protein such as insulin, human growth hormone, interferon. 7 Uses For Transgenic Organisms • Transgenic Bacteria – Researchers may need a particular protein in large quantities for research. – A pharmaceutical may wish to produce large quantities of growth hormone or insulin. – Bacteria which digests toxins and pollutants such as oil and sewage. Uses For Transgenic Organisms • Transgenic Plants – Genes can be inserted in to the plant DNA by a bacterium which infects plants. – Natural insecticides such as BT – Plants which produce their own fertilizer – Fruits and vegetables which don’t spoil as quickly. • Transgenic Animals – DNA is inserted into the nucleus of a fertilized egg cell. – Animals for research. 8 Cloning an Entire Organism • Clone – A newborn individual is a genetic copy of the adult. – Produce large numbers of organisms which have favorable characteristics. – Save an endangered species • Remove the nucleus from an egg cell replace the nucleus with a nucleus from an adult organism Place the egg back into the foster mother. Cloning an Entire Organism 9 Gel Electrophoresis • • • • • • • Used to determine the size of DNA fragments DNA samples are run through a porous gel called agarose. The DNA is pulled through the agarose by running an electric current through the agarose gel. DNA has a negative charge DNA molecules migrate toward the anode which has a positive charge Large fragments of DNA move slowly through the agarose while small DNA fragments move quickly. A molecular weight marker is used to estimate the size of the DNA fragments Gel Electrophoresis 10 Gel Electrophoresis Gel Electrophoresis • Uses for gel electrophoresis – Identify similarities and differences among different kinds of organisms. – DNA fingerprinting. – Separate DNA by size. – Determine the sequence of an organism’s DNA 11 Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) • PCR = Polymerase chain reaction • A lab technique which produces millions of copies of DNA. • Can be used for many applications including – DNA fingerprinting – Diagnosis of diseases 12 Gene Therapy • Gene therapy - using DNA in order to treat a disease. • A functional gene replaces a mutated gene. • Gene therapy treatments are becoming more and more successful as research progresses. 13